4. ゲームサンプル¶
たった数十~数百行のコードで本格的なゲームを開発できるのが Siv3D の特徴です。いくつかの例を動かしてみましょう。
ソースコードをクリップボードにコピーするには、コードの右上の をクリックします。
4.1 ブロックくずし¶
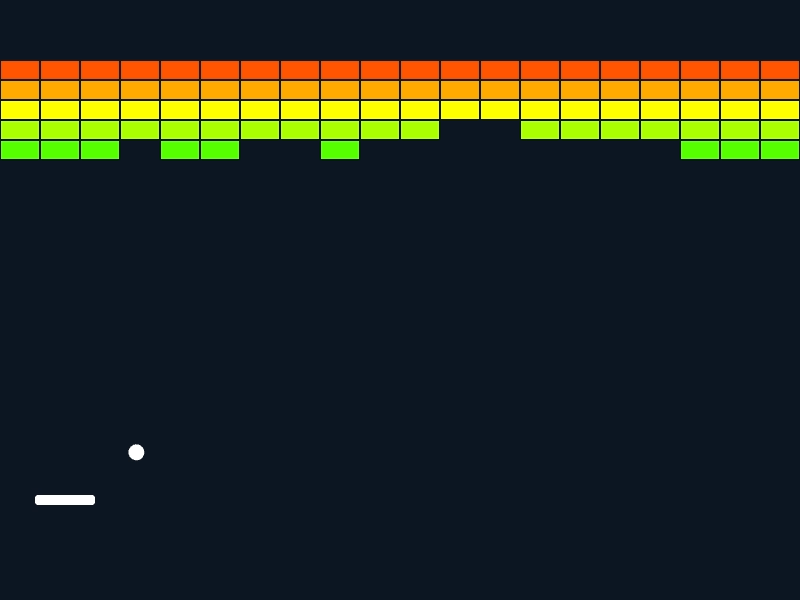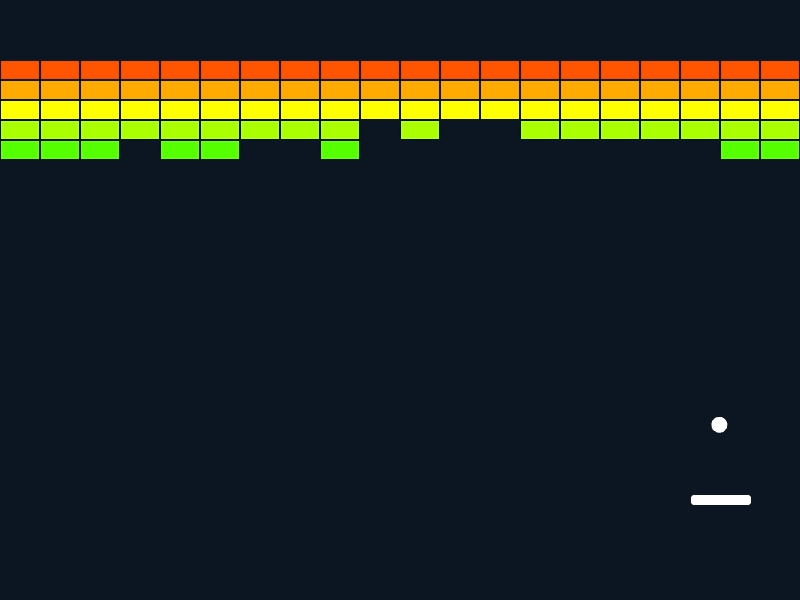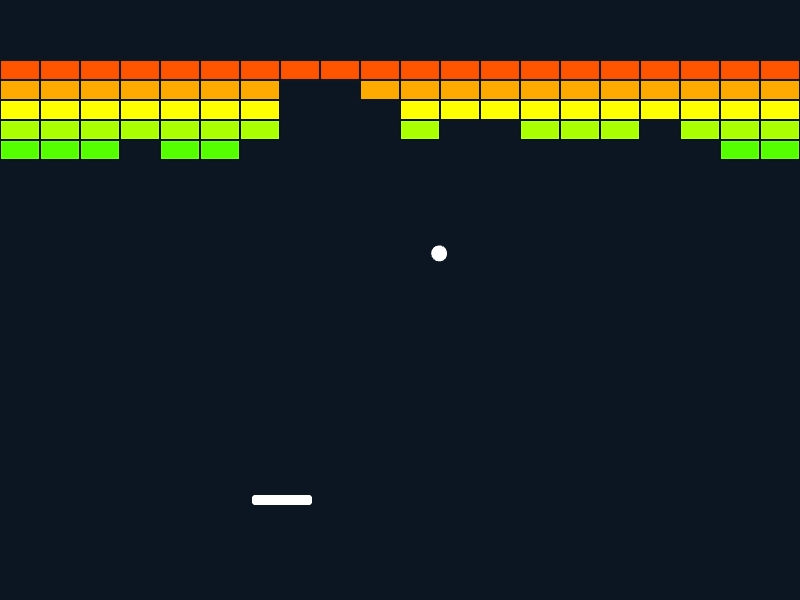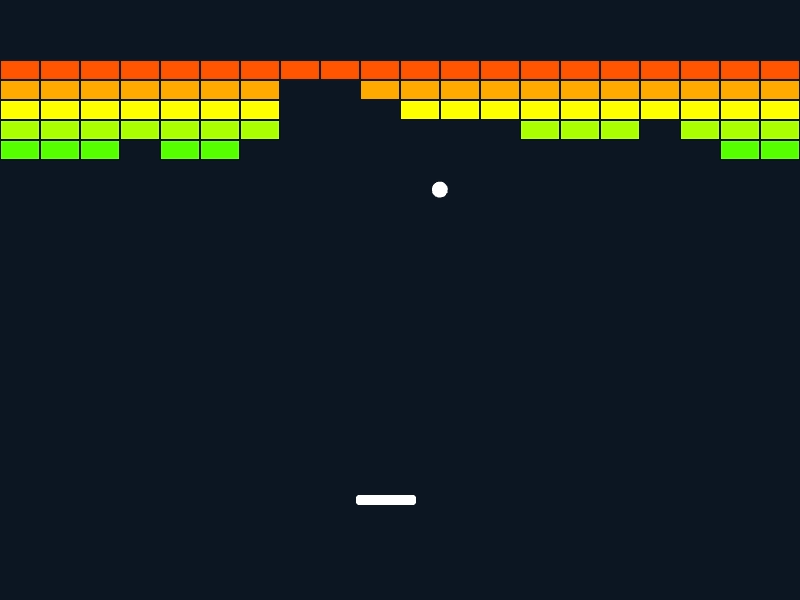
Siv3D でのゲームプログラミングの雰囲気を体験できる、ブロックくずしのサンプルです。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
// 1 つのブロックのサイズ
constexpr Size BrickSize{ 40, 20 };
// ボールの速さ(ピクセル / 秒)
constexpr double BallSpeedPerSec = 480.0;
// ボールの速度
Vec2 ballVelocity{ 0, -BallSpeedPerSec };
// ボール
Circle ball{ 400, 400, 8 };
// ブロックの配列
Array<Rect> bricks;
for (int32 y = 0; y < 5; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / BrickSize.x); ++x)
{
bricks << Rect{ (x * BrickSize.x), (60 + y * BrickSize.y), BrickSize };
}
}
while (System::Update())
{
// パドル
const Rect paddle{ Arg::center(Cursor::Pos().x, 500), 60, 10 };
// ボールを移動させる
ball.moveBy(ballVelocity * Scene::DeltaTime());
// ブロックを順にチェックする
for (auto it = bricks.begin(); it != bricks.end(); ++it)
{
// ブロックとボールが交差していたら
if (it->intersects(ball))
{
// ブロックの上辺、または底辺と交差していたら
if (it->bottom().intersects(ball) || it->top().intersects(ball))
{
// ボールの速度の Y 成分の符号を反転する
ballVelocity.y *= -1;
}
else // ブロックの左辺または右辺と交差していたら
{
// ボールの速度の X 成分の符号を反転する
ballVelocity.x *= -1;
}
// ブロックを配列から削除する(イテレータは無効になる)
bricks.erase(it);
// これ以上チェックしない
break;
}
}
// 天井にぶつかったら
if ((ball.y < 0) && (ballVelocity.y < 0))
{
// ボールの速度の Y 成分の符号を反転する
ballVelocity.y *= -1;
}
// 左右の壁にぶつかったら
if (((ball.x < 0) && (ballVelocity.x < 0))
|| ((Scene::Width() < ball.x) && (0 < ballVelocity.x)))
{
// ボールの速度の X 成分の符号を反転する
ballVelocity.x *= -1;
}
// パドルにあたったら
if ((0 < ballVelocity.y) && paddle.intersects(ball))
{
// パドルの中心からの距離に応じてはね返る方向(速度ベクトル)を変える
ballVelocity = Vec2{ (ball.x - paddle.center().x) * 10, -ballVelocity.y }.withLength(BallSpeedPerSec);
}
// すべてのブロックを描画する
for (const auto& brick : bricks)
{
// ブロックの Y 座標に応じて色を変える
brick.stretched(-1).draw(HSV{ brick.y - 40 });
}
// マウスカーソルを非表示にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hidden);
// ボールを描く
ball.draw();
// パドルを描く
paddle.rounded(3).draw();
}
}
よりコンパクトになるよう書き換えると次のようになります。各種ゲームエンジン・ゲームフレームワークの中でも、この短さ(25 LoC)でブロックくずしを動かせるのは Siv3D だけです。
コンパクトにしたコード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Vec2 velocity{ 0, -480 };
Circle ball{ 400, 400, 8 };
Array<Rect> bricks;
for (auto p : step(Size{ 20, 5 }))
{
bricks << Rect{ (p.x * 40), (60 + p.y * 20), 40, 20 };
}
while (System::Update())
{
const Rect paddle{ Arg::center(Cursor::Pos().x, 500), 60, 10 };
ball.moveBy(velocity * Scene::DeltaTime());
for (auto it = bricks.begin(); it != bricks.end(); ++it)
{
if (it->intersects(ball))
{
((it->bottom().intersects(ball) || it->top().intersects(ball)) ? velocity.y : velocity.x) *= -1;
bricks.erase(it);
break;
}
}
if ((ball.y < 0) && (velocity.y < 0))
{
velocity.y *= -1;
}
if (((ball.x < 0) && (velocity.x < 0)) || ((Scene::Width() < ball.x) && (0 < velocity.x)))
{
velocity.x *= -1;
}
if ((0 < velocity.y) && paddle.intersects(ball))
{
velocity = Vec2{ (ball.x - paddle.center().x) * 10, -velocity.y }.withLength(480);
}
for (const auto& brick : bricks)
{
brick.stretched(-1).draw(HSV{ brick.y - 40 });
}
ball.draw();
paddle.rounded(3).draw();
}
}
4.2 タイピングゲーム¶

タイピングゲームの基本機能は次のように実装できます。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// 問題文のリスト
const Array<String> texts =
{
U"Practice makes perfect.",
U"Don't cry over spilt milk.",
U"Faith will move mountains.",
U"Nothing ventured, nothing gained.",
U"Bad news travels fast.",
};
// 問題文をランダムに選ぶ
String target = texts.choice();
// 入力中の文字列
String input;
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
while (System::Update())
{
// テキスト入力(TextInputMode::DenyControl: エンターやタブ、バックスペースは受け付けない)
TextInput::UpdateText(input, TextInputMode::DenyControl);
// 誤った入力が含まれていたら削除する
while (not target.starts_with(input))
{
input.pop_back();
}
// 一致したら次の問題へ移る
if (input == target)
{
// 問題文をランダムに選ぶ
target = texts.choice();
// 入力文字列をクリアする
input.clear();
}
// 問題文を描画する
font(target).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 80 }, ColorF{ 0.98 });
// 入力中の文字を描画する
font(input).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 80 }, ColorF{ 0.12 });
}
}
ゲームループ内でやりたいこと(テキスト入力の更新、描画、ステート更新)が、そのまま直感的にコードに反映されている点が特徴です。システム周りや低レベル API との格闘をほとんど必要とせず、アイデア検証そのものに集中でき、プロトタイプ制作の生産性を高めることができます。
4.3 絵文字タワー¶

次のプログラムは「絵文字をクリックでドロップし、物理的に積み上がるタワー」を作るという一連の機能(画像からポリゴン生成、物理シミュレーション、カメラ操作、描画)を、コンパクトなコードで完結させています。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
// ウィンドウを 1280x720 にリサイズ
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
// 背景色を設定
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.2, 0.7, 1.0 });
// 登場する絵文字
const Array<String> emojis = { U"🐘", U"🐧", U"🐐", U"🐤" };
Array<MultiPolygon> polygons;
Array<Texture> textures;
for (const auto& emoji : emojis)
{
// 絵文字の画像から形状情報を作成する
polygons << Emoji::CreateImage(emoji).alphaToPolygonsCentered().simplified(2.0);
// 絵文字の画像からテクスチャを作成する
textures << Texture{ Emoji{ emoji } };
}
// 2D 物理演算のシミュレーションステップ(秒)
constexpr double StepTime = (1.0 / 200.0);
// 2D 物理演算のシミュレーション蓄積時間(秒)
double accumulatedTime = 0.0;
// 2D 物理演算のワールド
P2World world;
// [_] 地面
const P2Body ground = world.createLine(P2Static, Vec2{ 0, 0 }, Line{ -300, 0, 300, 0 });
// 動物の物体
Array<P2Body> bodies;
// 物体の ID と絵文字のインデックスの対応テーブル
HashTable<P2BodyID, size_t> table;
// 絵文字のインデックス
size_t index = Random(polygons.size() - 1);
// 2D カメラ
Camera2D camera{ Vec2{ 0, -200 } };
while (System::Update())
{
accumulatedTime += Scene::DeltaTime();
while (StepTime <= accumulatedTime)
{
// 2D 物理演算のワールドを更新する
world.update(StepTime);
accumulatedTime -= StepTime;
}
// 地面より下に落ちた物体は削除する
for (auto it = bodies.begin(); it != bodies.end();)
{
if (100 < it->getPos().y)
{
// 対応テーブルからも削除する
table.erase(it->id());
it = bodies.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
// 2D カメラを更新する
camera.update();
{
// 2D カメラから Transformer2D を作成する
const auto t = camera.createTransformer();
// 左クリックされたら
if (MouseL.down())
{
// ボディを追加する
bodies << world.createPolygons(P2Dynamic, Cursor::PosF(), polygons[index], P2Material{ 0.1, 0.0, 1.0 });
// ボディ ID と絵文字のインデックスの組を対応テーブルに追加する
table.emplace(bodies.back().id(), std::exchange(index, Random(polygons.size() - 1)));
}
// すべてのボディを描画する
for (const auto& body : bodies)
{
textures[table[body.id()]].rotated(body.getAngle()).drawAt(body.getPos());
}
// 地面を描画する
ground.draw(Palette::Green);
// 現在操作できる絵文字を描画する
textures[index].drawAt(Cursor::PosF(), AlphaF(0.5 + Periodic::Sine0_1(1s) * 0.5));
}
// 2D カメラの操作を描画する
camera.draw(Palette::Orange);
}
}
-
直感的でシンプルな API 設計
world.createPolygons(...)のように、物理空間へオブジェクトを配置する操作が「配列へ要素を push する」程度の感覚で行えます。カメラ操作 (Camera2D camera) や描画 (.drawAt()) も、特別な下準備や複雑なハンドリングをせずに利用でき、開発者はビジュアル的・物理的な要素を直感的に組み上げられます。 -
ビルトイン機能の統合性と拡張性
絵文字からポリゴンを生成し、物理シミュレーションへ組み込むといった「画像 ⇒ 形状 ⇒ 物理オブジェクト」という流れをEmoji::CreateImage().alphaToPolygonsCentered()という標準の API だけで実現できます。ゲーム制作に必要な工程(テクスチャ読み込み、形状抽出、物理モデルへの変換)をワンストップで行い、クリエイターがアイデア実装に集中できるようにしています。 -
インタラクションと描画、物理、カメラといった要素間のシームレスな連携
UI 操作(マウスクリック)、物理シミュレーション、視界操作(カメラ)、そして視覚表現(テクスチャ描画)を自然な形で統合しています。これらはしばしば別々のレイヤーで扱われがちですが、Siv3D はこれらをまとめることで、学習コストやグルーコードを減らしています。 -
軽量なプロトタイピングへの適合
複雑なリソース管理、初期化コード、設定ファイルなどがほぼ登場せず、読みやすい単一ファイルで動作します。Siv3D はアイデアを即時に試し、すぐに手直しできる、プロトタイピングに適したツールです。ゲームジャムや教育現場、初学者の学習など、スピードと簡便さが求められる場面で特に有効です。
4.4 スロットマシン¶

Space で操作するスロットマシンのサンプルです。
効果音は標準搭載のサウンドフォントを使ってプログラムで生成しています。コードのハイライト部分を改造することで、絵柄や出現確率、賞金などの設定を変更できます。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief スロットゲームの絵柄
struct Symbol
{
/// @brief 絵柄
Texture symbol;
/// @brief 賞金
int32 score;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// フォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48,
U"example/font/RocknRoll/RocknRollOne-Regular.ttf" };
// ゲーム開始の効果音
const Audio soundStart{ Wave{ GMInstrument::Agogo,
PianoKey::A3, 0.3s, 0.2s } };
// リール停止の効果音
const Audio soundStop{ Wave{ GMInstrument::SteelDrums,
PianoKey::A3, 0.3s, 0.2s } };
// 賞金獲得の効果音(ループ再生)
const Audio soundGet{ Wave{ GMInstrument::TinkleBell,
PianoKey::A6, 0.1s, 0.0s }, Loop::Yes };
// 絵柄のリスト
const Array<Symbol> symbols
{
{ Texture{ U"💎"_emoji }, 1000 },
{ Texture{ U"7️⃣"_emoji }, 777 },
{ Texture{ U"💰"_emoji }, 300 },
{ Texture{ U"🃏"_emoji }, 100 },
{ Texture{ U"🍇"_emoji }, 30 },
{ Texture{ U"🍒"_emoji }, 10 },
};
// 1 つのリールに用意される絵柄の基本リスト
const Array<int32> symbolListBase =
{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5 };
// 3 つのリールに用意される絵柄のリスト(基本リストをシャッフル)
const std::array<Array<int32>, 3> symbolLists =
{
symbolListBase.shuffled(),
symbolListBase.shuffled(),
symbolListBase.shuffled()
};
// 3 つのリールの描画位置
const std::array<Rect, 3> reels
{
Rect{ 80, 100, 130, 300 },
Rect{ 230, 100, 130, 300 },
Rect{ 380, 100, 130, 300 },
};
// 所持金の描画位置
const RoundRect moneyRect{ 560, 440, 190, 60, 20 };
// 3 つのリールの回転量
std::array<double, 3> rolls = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
// 現在のゲームにおけるリール停止カウント(3 回で結果判定)
int32 stopCount = 3;
// 所持金
int32 money = 1000;
while (System::Update())
{
// スペースキーが押されたら
if (KeySpace.down())
{
// 3 つのリールが停止している場合
if (stopCount == 3)
{
// 所持金が 3 以上ある場合
if (3 <= money)
{
// 所持金を 3 減らす
money -= 3;
// リール停止回数を 0 に戻す
stopCount = 0;
// ゲーム開始の効果音を再生する
soundStart.playOneShot();
}
}
else
{
// リールを整数位置で停止させる
rolls[stopCount] = Math::Ceil(rolls[stopCount]);
// リール停止カウントを増やす
++stopCount;
// リール停止の効果音を再生する
soundStop.playOneShot();
// 3 つのリールが停止した場合
if (stopCount == 3)
{
// 各リールの絵柄
const int32 r0 = symbolLists[0][(
static_cast<int32>(rolls[0] + 1) % symbolLists[0].size())];
const int32 r1 = symbolLists[1][(
static_cast<int32>(rolls[1] + 1) % symbolLists[1].size())];
const int32 r2 = symbolLists[2][(
static_cast<int32>(rolls[2] + 1) % symbolLists[2].size())];
// 3 つのリールの絵柄がすべて同じ場合
if ((r0 == r1) && (r1 == r2))
{
// 所持金に賞金を加算する
money += symbols[r0].score;
// 賞金獲得の効果音を再生する
soundGet.play();
// 賞金獲得の効果音を 1.5 秒後に停止する
soundGet.stop(1.5s);
}
}
}
}
// リールの回転
for (int32 i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
// 停止済みのリールはスキップ
if (i < stopCount)
{
continue;
}
// 前フレームからの経過時間に応じてリールの回転量を増やす
rolls[i] += (Scene::DeltaTime() * 12);
}
// リールの描画
for (int32 k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
{
// リールの背景
reels[k].draw();
// リールの絵柄を描画
for (int32 i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
// リールの何番目の要素を指すか(回転量の整数部分)
const int32 index = (static_cast<int32>(rolls[k] + i)
% symbolLists[k].size());
// 絵柄のインデックス
const int32 symbolIndex = symbolLists[k][index];
// 絵柄の位置補正(回転量の小数部分)
const double t = Math::Fraction(rolls[k]);
// 絵柄の描画
symbols[symbolIndex].symbol.resized(90)
.drawAt(reels[k].center().movedBy(0, 140 * (1 - i + t)));
}
}
// リールの上下に背景色を描くことで、はみ出した絵柄を隠す
Rect{ 80, 0, 430, 100 }.draw(Scene::GetBackground());
Rect{ 80, 400, 430, 200 }.draw(Scene::GetBackground());
// リールの影と枠線の描画
for (const auto& reel : reels)
{
// 上の影
Rect{ reel.tl(), reel.w, 40 }.draw(Arg::top(0.0, 0.3), Arg::bottom(0.0, 0.0));
// 下の影
Rect{ (reel.bl() - Point{ 0, 40 }), reel.w, 40 }.draw(Arg::top(0.0, 0.0), Arg::bottom(0.0, 0.3));
// 枠線
reel.drawFrame(4, ColorF{ 0.5 });
}
// 中央を指す 2 つの三角形の描画
Triangle{ 60, 250, 36, 90_deg }.draw(ColorF{ 1.0, 0.2, 0.2 });
Triangle{ 530, 250, 36, -90_deg }.draw(ColorF{ 1.0, 0.2, 0.2 });
// 絵柄リストを描く
RoundRect{ 560, 100, 190, 300, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.9, 0.95, 1.0 });
for (size_t i = 0; i < symbols.size(); ++i)
{
// 絵柄を描く
symbols[i].symbol.resized(32).draw(Vec2{ 586, (114 + i * 48) });
// 賞金を描く
font(symbols[i].score).draw(TextStyle::OutlineShadow(0.2, ColorF{ 0.5, 0.3, 0.2 },
Vec2{ 1.5, 1.5 }, ColorF{ 0.5, 0.3, 0.2 }),
25, Arg::topRight(720, (109 + i * 48)), ColorF{ 1.0, 0.9, 0.1 });
if (i != 0)
{
// 絵柄の間に区切り線を描く
Rect{ 570, (105 + i * 48), 170, 1 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.7 });
}
}
// 所持金の背景の描画
if (soundGet.isPlaying())
{
// 賞金獲得中は点滅させる
const ColorF color = Periodic::Sine0_1(0.3s) * ColorF { 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 };
moneyRect.draw(color).drawFrame(1);
}
else
{
moneyRect.draw(ColorF{ 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 }).drawFrame(1);
}
// 所持金の描画
font(money).draw(30, Arg::rightCenter(moneyRect.rightCenter().movedBy(-30, 0)));
}
}
4.5 クッキークリッカー¶
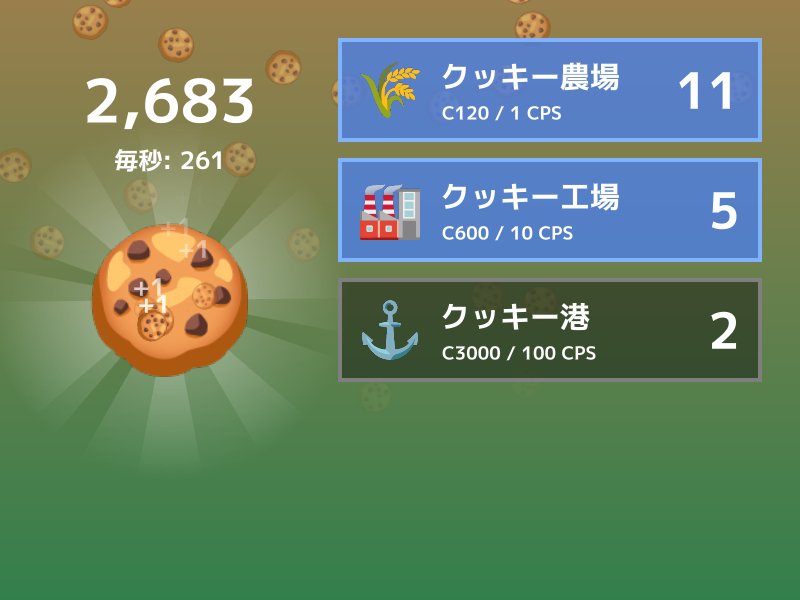
クリックと生産設備の購入でアイテムの数を増やす「クッキークリッカー」系ゲームのサンプルです。
セーブデータのシリアライズや、エフェクトの作成、アイテムボタンの UI など、多彩な機能が個々の関数やクラスに整理されています。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
// ゲームのセーブデータ
struct SaveData
{
double cookies;
Array<int32> itemCounts;
// シリアライズに対応させるためのメンバ関数を定義する
template <class Archive>
void SIV3D_SERIALIZE(Archive& archive)
{
archive(cookies, itemCounts);
}
};
/// @brief アイテムのボタン
/// @param rect ボタンの領域
/// @param texture ボタンの絵文字
/// @param font 文字描画に使うフォント
/// @param name アイテムの名前
/// @param desc アイテムの説明
/// @param count アイテムの所持数
/// @param enabled ボタンを押せるか
/// @return ボタンが押された場合 true, それ以外の場合は false
bool Button(const Rect& rect, const Texture& texture, const Font& font, const String& name, const String& desc, int32 count, bool enabled)
{
if (enabled)
{
rect.draw(ColorF{ 0.3, 0.5, 0.9, 0.8 });
rect.drawFrame(2, 2, ColorF{ 0.5, 0.7, 1.0 });
if (rect.mouseOver())
{
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
}
else
{
rect.draw(ColorF{ 0.0, 0.4 });
rect.drawFrame(2, 2, ColorF{ 0.5 });
}
texture.scaled(0.5).drawAt(rect.x + 50, rect.y + 50);
font(name).draw(30, rect.x + 100, rect.y + 15, Palette::White);
font(desc).draw(18, rect.x + 102, rect.y + 60, Palette::White);
font(count).draw(50, Arg::rightCenter((rect.x + rect.w - 20), (rect.y + 50)), Palette::White);
return (enabled && rect.leftClicked());
}
// クッキーが降るエフェクト
struct CookieBackgroundEffect : IEffect
{
// 初期座標
Vec2 m_start;
// 回転角度
double m_angle;
// テクスチャ
Texture m_texture;
CookieBackgroundEffect(const Vec2& start, const Texture& texture)
: m_start{ start }
, m_angle{ Random(2_pi) }
, m_texture{ texture } {
}
bool update(double t) override
{
const Vec2 pos = m_start + 0.5 * t * t * Vec2{ 0, 120 };
m_texture.scaled(0.3).rotated(m_angle).drawAt(pos, ColorF{ 1.0, (1.0 - t / 3.0) });
return (t < 3.0);
}
};
// クッキーが舞うエフェクト
struct CookieEffect : IEffect
{
// 初期座標
Vec2 m_start;
// 初速
Vec2 m_velocity;
// 拡大倍率
double m_scale;
// 回転角度
double m_angle;
// テクスチャ
Texture m_texture;
CookieEffect(const Vec2& start, const Texture& texture)
: m_start{ start }
, m_velocity{ Circular{ 80, Random(-40_deg, 40_deg) } }
, m_scale{ Random(0.2, 0.3) }
, m_angle{ Random(2_pi) }
, m_texture{ texture } {
}
bool update(double t) override
{
const Vec2 pos = m_start
+ m_velocity * t + 0.5 * t * t * Vec2{ 0, 120 };
m_texture.scaled(m_scale).rotated(m_angle).drawAt(pos, ColorF{ 1.0, (1.0 - t) });
return (t < 1.0);
}
};
// 「+1」が上昇するエフェクト
struct PlusOneEffect : IEffect
{
// 初期座標
Vec2 m_start;
// フォント
Font m_font;
PlusOneEffect(const Vec2& start, const Font& font)
: m_start{ start }
, m_font{ font } {
}
bool update(double t) override
{
m_font(U"+1").drawAt(24, m_start.movedBy(0, t * -120), ColorF{ 1.0, (1.0 - t) });
return (t < 1.0);
}
};
// アイテムのデータ
struct Item
{
// アイテムの絵文字
Texture emoji;
// アイテムの名前
String name;
// アイテムを初めて購入するときのコスト
int32 initialCost;
// アイテムの CPS
int32 cps;
// アイテムを count 個持っているときの購入コストを返す
int32 getCost(int32 count) const
{
return initialCost * (count + 1);
}
};
// クッキーのばね
class CookieSpring
{
public:
void update(double deltaTime, bool pressed)
{
// ばねの蓄積時間を加算する
m_accumulatedTime += deltaTime;
while (0.005 <= m_accumulatedTime)
{
// ばねの力(変化を打ち消す方向)
double force = (-0.02 * m_x);
// 画面を押しているときに働く力
if (pressed)
{
force += 0.004;
}
// 速度に力を適用(減衰もさせる)
m_velocity = (m_velocity + force) * 0.92;
// 位置に反映
m_x += m_velocity;
m_accumulatedTime -= 0.005;
}
}
double get() const
{
return m_x;
}
private:
// ばねの伸び
double m_x = 0.0;
// ばねの速度
double m_velocity = 0.0;
// ばねの蓄積時間
double m_accumulatedTime = 0.0;
};
// クッキーの後光を描く関数
void DrawHalo(const Vec2& center)
{
for (int32 i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
double startAngle = Scene::Time() * 15_deg + i * 90_deg;
Circle{ center, 180 }.drawPie(startAngle, 60_deg, ColorF{ 1.0, 0.3 }, ColorF{ 1.0, 0.0 });
}
for (int32 i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
{
double startAngle = Scene::Time() * -15_deg + i * 60_deg;
Circle{ center, 180 }.drawPie(startAngle, 40_deg, ColorF{ 1.0, 0.3 }, ColorF{ 1.0, 0.0 });
}
}
// アイテムの所有数をもとに CPS を計算する関数
int32 CalculateCPS(const Array<Item>& ItemTable, const Array<int32>& itemCounts)
{
int32 cps = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < ItemTable.size(); ++i)
{
cps += ItemTable[i].cps * itemCounts[i];
}
return cps;
}
void Main()
{
// クッキーの絵文字
const Texture texture{ U"🍪"_emoji };
// アイテムのデータ
const Array<Item> ItemTable = {
{ Texture{ U"🌾"_emoji }, U"クッキー農場", 10, 1 },
{ Texture{ U"🏭"_emoji }, U"クッキー工場", 100, 10 },
{ Texture{ U"⚓"_emoji }, U"クッキー港", 1000, 100 },
};
// 各アイテムの所有数
Array<int32> itemCounts(ItemTable.size()); // = { 0, 0, 0 }
// フォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
// クッキーのクリック円
constexpr Circle CookieCircle{ 170, 300, 100 };
// エフェクト
Effect effectBackground, effect;
// クッキーのばね
CookieSpring cookieSpring;
// クッキーの個数
double cookies = 0;
// ゲームの経過時間の蓄積
double accumulatedTime = 0.0;
// 背景のクッキーの蓄積時間
double cookieBackgroundAccumulatedTime = 0.0;
// セーブデータが見つかればそれを読み込む
{
// バイナリファイルをオープン
Deserializer<BinaryReader> reader{ U"game.save" };
if (reader) // もしオープンに成功したら
{
SaveData saveData;
reader(saveData);
cookies = saveData.cookies;
for (size_t i = 0; i < Min(ItemTable.size(), saveData.itemCounts.size()); ++i)
{
itemCounts[i] = saveData.itemCounts[i];
}
}
}
while (System::Update())
{
// クッキーの毎秒の生産量を計算する
const int32 cps = CalculateCPS(ItemTable, itemCounts);
// ゲームの経過時間を加算する
accumulatedTime += Scene::DeltaTime();
// 0.1 秒以上蓄積していたら
if (0.1 <= accumulatedTime)
{
accumulatedTime -= 0.1;
// 0.1 秒分のクッキー生産を加算する
cookies += (cps * 0.1);
}
// 背景のクッキー
{
// 背景のクッキーが発生する適当な間隔を cps から計算(多くなりすぎないよう緩やかに小さくなり、下限も設ける)
const double cookieBackgroundSpawnTime = cps ? Max(1.0 / Math::Log2(cps * 2), 0.03) : Math::Inf;
if (cps)
{
cookieBackgroundAccumulatedTime += Scene::DeltaTime();
}
while (cookieBackgroundSpawnTime <= cookieBackgroundAccumulatedTime)
{
effectBackground.add<CookieBackgroundEffect>(RandomVec2(Rect{ 0, -150, 800, 100 }), texture);
cookieBackgroundAccumulatedTime -= cookieBackgroundSpawnTime;
}
}
// クッキーのばねを更新する
cookieSpring.update(Scene::DeltaTime(), CookieCircle.leftPressed());
// クッキー円上にマウスカーソルがあれば
if (CookieCircle.mouseOver())
{
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// クッキー円が左クリックされたら
if (CookieCircle.leftClicked())
{
++cookies;
// クッキーが舞うエフェクトを追加する
effect.add<CookieEffect>(Cursor::Pos().movedBy(Random(-5, 5), Random(-5, 5)), texture);
// 「+1」が上昇するエフェクトを追加する
effect.add<PlusOneEffect>(Cursor::Pos().movedBy(Random(-5, 5), Random(-15, -5)), font);
// 背景のクッキーを追加する
effectBackground.add<CookieBackgroundEffect>(RandomVec2(Rect{ 0, -150, 800, 100 }), texture);
}
// 背景を描く
Rect{ 0, 0, 800, 600 }.draw(Arg::top = ColorF{ 0.6, 0.5, 0.3 }, Arg::bottom = ColorF{ 0.2, 0.5, 0.3 });
// 背景で降り注ぐクッキーを描画する
effectBackground.update();
// クッキーの後光を描く
DrawHalo(CookieCircle.center);
// クッキーの数を整数で表示する
font(ThousandsSeparate((int32)cookies)).drawAt(60, 170, 100);
// クッキーの生産量を表示する
font(U"毎秒: {}"_fmt(cps)).drawAt(24, 170, 160);
// クッキーを描画する
texture.scaled(1.5 - cookieSpring.get()).drawAt(CookieCircle.center);
// エフェクトを描画する
effect.update();
for (size_t i = 0; i < ItemTable.size(); ++i)
{
// アイテムの所有数
const int32 itemCount = itemCounts[i];
// アイテムの現在の価格
const int32 itemCost = ItemTable[i].getCost(itemCount);
// アイテム 1 つあたりの CPS
const int32 itemCps = ItemTable[i].cps;
// ボタン
if (Button(Rect{ 340, (40 + 120 * i), 420, 100 }, ItemTable[i].emoji,
font, ItemTable[i].name, U"C{} / {} CPS"_fmt(itemCost, itemCps), itemCount, (itemCost <= cookies)))
{
cookies -= itemCost;
++itemCounts[i];
}
}
}
// メインループの後、終了時にゲームをセーブ
{
// バイナリファイルをオープン
Serializer<BinaryWriter> writer{ U"game.save" };
// シリアライズに対応したデータを書き出す
writer(SaveData{ cookies, itemCounts });
}
}
4.6 マインスイーパー¶
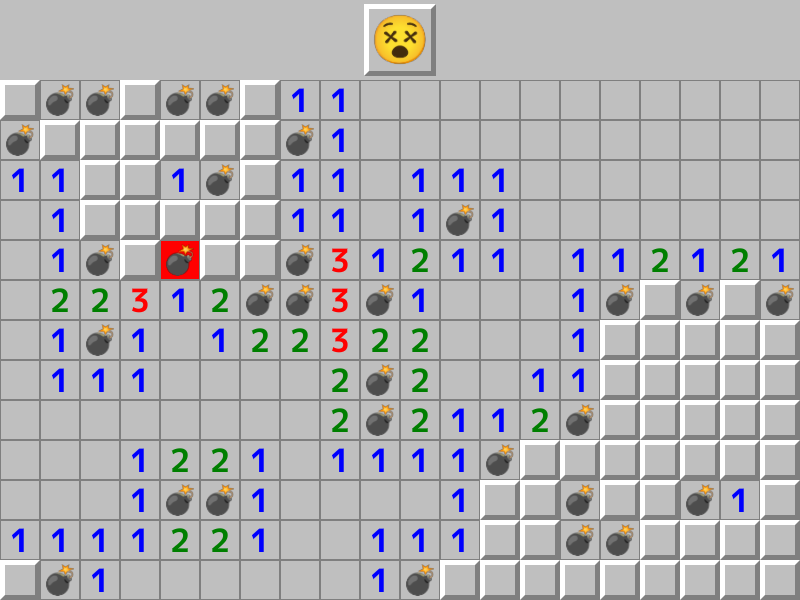
クラシカルなマインスイーパーのサンプルです。マウスの左クリックでセルを開き、右クリックで旗を立てます。爆弾を踏まないように、爆弾の位置を推測しながらセルを開いていきます。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
// ゲームの状態
enum class GameState
{
Game, // ゲームが進行中
Failed, // ゲームオーバー
Cleared, // ゲームクリア
};
// セルの状態
struct CellState
{
// 開かれている
bool opened = false;
// 旗が立てられている
bool flagged = false;
// 爆発した
bool exploded = false;
// 島番号(数字のないマスを一気に開くときに使う)
int32 groupIndex = 0;
};
// 周囲のマスへのオフセット
constexpr Point Offsets[8] =
{
{ -1, -1 }, { 0, -1 }, { 1, -1 },
{ -1, 0 } , { 1, 0 },
{ -1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, 1 },
};
// 指定したマス目の周囲にある 💣 (-1) の個数を返す関数
int32 GetBombCount(const Grid<int32>& grid, const Point& center)
{
// 自身が 💣 (-1) なら -1 を返す
if (grid[center] == -1)
{
return -1;
}
// 見つかった 💣 (-1) の個数
int32 bombCount = 0;
for (const auto& offset : Offsets)
{
// 調べるマス
const Point pos = (center + offset);
// grid.fetch(pos, defaultValue) は、
// pos が範囲内の場合 grid[pos] を返し、それ以外の場合は defaultValue を返す
if (grid.fetch(pos, 0) == -1) // 💣 (-1) の場合
{
++bombCount;
}
}
return bombCount;
}
// 盤面を生成する関数
Grid<int32> MakeGame(const Size& size, int32 bombs)
{
// 盤面の二次元配列を作成する
Grid<int32> grid(size);
// 指定された個数だけ 💣 (-1) を設置する
while (bombs)
{
// 二次元配列上のランダムな位置
const Point pos = RandomPoint((size.x - 1), (size.y - 1));
// 未設置であれば
if (grid[pos] == 0)
{
// 💣 (-1) を設置する
grid[pos] = -1;
// 残りの 💣 の個数を減らす
--bombs;
}
}
// すべてのマスについて
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
// 数字を計算する。ただし、💣 マスは -1 のまま
grid[y][x] = GetBombCount(grid, Point{ x, y });
}
}
return grid;
}
// 盤面の状態を作成する関数
Grid<CellState> MakeStates(const Grid<int32>& grid)
{
const Size size = grid.size();
// 盤面と同じ大きさの二次元配列
Grid<CellState> states(size);
// 各マスの接続状況を管理するデータ構造
DisjointSet<int32> ds{ states.num_elements() };
// すべてのマスについて
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
// 自身のマスのインデックス
const int32 index = static_cast<int32>(y * size.x + x);
// 自身が 0 のマスで
if (grid[y][x] == 0)
{
// 右のマスが 0 なら
if (int nx = (x + 1);
(nx < size.x) && (grid[y][nx] == 0))
{
const int32 east = (index + 1); // 右のマスのインデックス
ds.merge(index, east); // 右のマスを同じ島にする
}
// 下のマスが 0 なら
if (int ny = (y + 1);
(ny < size.y) && (grid[ny][x] == 0))
{
const int32 south = (index + size.x); // 下のマスのインデックス
ds.merge(index, south); // 下のマスを同じ島にする
}
}
}
}
{
// マスのインデックス
int32 index = 0;
// すべてのマスについて
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
// 島番号を割り当て
states[y][x].groupIndex = ds.find(index);
++index;
}
}
}
return states;
}
// 開いていないセルのブロックを描く関数
void DrawBlock(const Rect& rect)
{
Triangle{ rect.tl(), rect.tr(), rect.bl() }.draw(ColorF{ 1.0 });
Triangle{ rect.tr(), rect.br(), rect.bl() }.draw(ColorF{ 0.5 });
rect.stretched(-5).draw(ColorF{ 0.75 });
}
// 盤面を描画する関数
void DrawGame(const Grid<int32>& grid, const Grid<CellState>& states, const Font& font, const Texture& bombTexture, const Texture& flagTexture, const Point& gamePos, const Size& cellSize)
{
// 0~8 の数字の色
constexpr ColorF NumberColors[9] =
{
ColorF{ 0, 0, 0 }, ColorF{ 0, 0, 1 }, ColorF{ 0, 0.5, 0 }, ColorF{ 1, 0, 0 },
ColorF{ 0, 0, 0.5 }, ColorF{ 0.5, 0, 0 }, ColorF{ 0.5, 0, 0 }, ColorF{ 0.5, 0, 0 }, ColorF{ 0.5, 0, 0 }
};
// すべてのマスについて
for (int32 y = 0; y < grid.height(); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < grid.width(); ++x)
{
const auto& state = states[y][x];
// セルの左上座標
const Point pos = (gamePos + (cellSize * Point{ x, y }));
// セルの領域
const Rect cell{ pos, cellSize };
if (state.opened) // 開かれている
{
// 背景を描く
cell.stretched(-1).draw(ColorF{ 0.75 });
if (const int32 n = grid[y][x];
n == -1) // 💣 (-1) マスであれば
{
// 爆発箇所であればセルを赤に
if (state.exploded)
{
cell.stretched(-1).draw(ColorF{ 1, 0, 0 });
}
// 爆弾を描く
bombTexture.resized(36).drawAt(cell.center());
}
else if (1 <= n) // 1 以上の数字マスであれば
{
// 数字を描く
font(n).drawAt(cell.center(), NumberColors[n]);
}
}
else // 開かれていない
{
// ブロックを描く
DrawBlock(cell);
// 旗が立てられているなら旗を描く
if (state.flagged)
{
flagTexture.resized(30).drawAt(cell.center());
}
}
}
}
}
// 指定された島番号のマスと、それらに隣接するマスを開く関数
void OpenGroup(const Grid<int32>& grid, Grid<CellState>& states, const int32 groupIndex)
{
// すべてのマスについて
for (int32 y = 0; y < grid.height(); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < grid.width(); ++x)
{
auto& state = states[y][x];
// 指定された島番号のマスであれば
if (state.groupIndex == groupIndex)
{
// 開く
state.opened = true;
// その周囲のマスについて
for (const auto& offset : Offsets)
{
const Point neighbor = (Point{ x, y } + offset);
// 盤面の範囲内かつ未開放であれば, そのマスも開く
if (grid.inBounds(neighbor) && (not states[neighbor].opened))
{
states[neighbor].opened = true;
// それが異なる島番号の数字のないマス (0) であれば, 再帰的にそれらも開く
if ((grid[neighbor] == 0) && (groupIndex != states[neighbor].groupIndex))
{
OpenGroup(grid, states, states[neighbor].groupIndex);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 盤面を更新する関数
void UpdateGame(GameState& gameState, const Grid<int32>& grid, Grid<CellState>& states, const int32 bombCount, const Point& gamePos, const Size& cellSize)
{
// 盤面の領域
const Rect gameArea{ gamePos, (grid.size() * cellSize - Point{ 1, 1 }) };
// 盤面が左クリックされた
const bool open = gameArea.leftClicked();
// 盤面が右クリックされた
const bool flag = gameArea.rightClicked();
if (open || flag)
{
// クリックされたマスの位置
const Point pos = ((Cursor::Pos() - gamePos) / cellSize);
if (open && (not states[pos].opened) && (not states[pos].flagged)) // 開かれていない、旗のないマスが左クリックされた
{
// そのマスを開く
states[pos].opened = true;
// そのマスが数字のないマス (0) であれば
if (grid[pos] == 0)
{
// 同じ島番号のマスと、それらに隣接するマスも開く
OpenGroup(grid, states, states[pos].groupIndex);
}
// そのマスが 💣 (-1) であれば
if (grid[pos] == -1)
{
// ゲームオーバーにする
gameState = GameState::Failed;
// 爆発したフラグを立てる
states[pos].exploded = true;
// すべての 💣 マスを開く
for (int32 y = 0; y < grid.height(); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < grid.width(); ++x)
{
if (grid[y][x] == -1)
{
states[y][x].opened = true;
}
}
}
}
else if (states.count_if([](const CellState& c) { return (not c.opened); }) == bombCount)
{ // 開かれていないマスの個数が爆弾の個数と一致すれば
// ゲームクリアにする
gameState = GameState::Cleared;
}
}
else if (flag) // 右クリックされた
{
// 旗の状態を反転
states[pos].flagged = (not states[pos].flagged);
}
}
}
void Main()
{
// 背景色をやや暗い灰色にする
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.5 });
// 盤面のマス目の数
constexpr Size GameSize{ 20, 13 };
// 設置する 💣 の個数
constexpr int32 BombCount = 30;
// 💣 の個数がマス目の 4 分の 1 以上の場合はコンパイルエラーにする
static_assert(BombCount < (GameSize.area() / 4));
// セルの大きさ
constexpr Size CellSize{ 40, 40 };
// 盤面の描画位置
constexpr Size GamePos{ 0, 80 };
// 数字用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 32, Typeface::Bold };
// 爆弾の絵文字
const Texture bombTexture{ U"💣"_emoji };
// 旗の絵文字
const Texture flagTexture{ U"🚩"_emoji };
// GameState に対応する顔絵文字
const std::array<Texture, 3> faceTextures = { Texture{ U"🙂"_emoji }, Texture{ U"😵"_emoji }, Texture{ U"😎"_emoji } };
// 盤面を作成する
Grid<int32> grid = MakeGame(GameSize, BombCount);
// 各セルの状態を作成する
Grid<CellState> states = MakeStates(grid);
// ゲームの状態
GameState gameState = GameState::Game;
// 顔ボタンの領域
const Rect faceButton{ Arg::center(Scene::Width() / 2, 40), 72 };
while (System::Update())
{
////////////////////////////////
//
// 状態の更新
//
////////////////////////////////
{
// ゲームが進行中なら盤面を更新
if (gameState == GameState::Game)
{
UpdateGame(gameState, grid, states, BombCount, GamePos, CellSize);
}
// 顔ボタンが押されたら状態を初期化
if (faceButton.leftClicked())
{
grid = MakeGame(GameSize, BombCount);
states = MakeStates(grid);
gameState = GameState::Game;
}
}
////////////////////////////////
//
// 描画
//
////////////////////////////////
{
// 盤面を描く
DrawGame(grid, states, font, bombTexture, flagTexture, GamePos, CellSize);
// UI エリアの背景を描く
Rect{ Scene::Width(), 80 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.75 });
{
// 顔ボタンを描く
DrawBlock(faceButton);
// 顔を描く
faceTextures[FromEnum(gameState)].resized(60).drawAt(faceButton.center());
}
}
}
}
4.7 AI オセロ¶
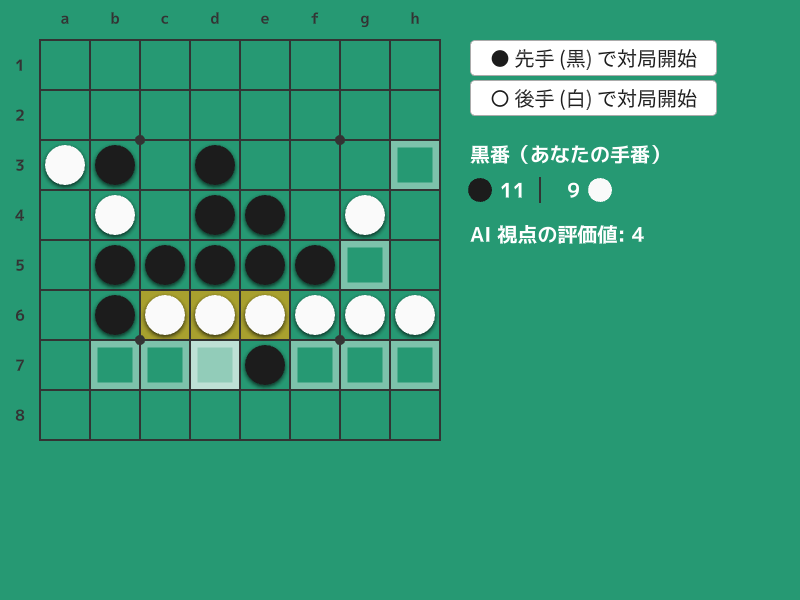
AI と対戦できるオセロのサンプルです。
オセロ AI の研究者である筑波大学の山名琢翔さんから、3 桁行におさまりながらも強い思考ルーチンを持つ AI のコードを提供してもらいました。ハイライト箇所(800 行目)の数値を変更することで、AI の強さを調整できます。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
namespace OthelloAI
{
// ビットボード
using BitBoard = uint64;
/// @brief ビットボード上のインデックス
/// @remark A1 が 63, B1 が 62, C1 が 61, ... H8 が 0
using BitBoardIndex = uint8;
/// @brief セルのインデックス
/// @remark A1 が 0, B1 が 1, C1 が 2, ... H8 が 63
using CellIndex = int32;
/// @brief 色
enum class Color
{
Black,
White
};
/// @brief 反対の色を返します。
/// @param c 色
/// @return 反対の色
[[nodiscard]]
constexpr Color operator ~(Color c)
{
return ((c == Color::Black) ? Color::White : Color::Black);
}
/// @brief セルのインデックスをビットボード上のインデックスに変換します。
/// @param i セルのインデックス
/// @return ビットボード上のインデックス
[[nodiscard]]
constexpr BitBoardIndex ToBitBoardIndex(CellIndex i)
{
return static_cast<BitBoardIndex>(63 - i);
}
/// @brief ビットボード上のインデックスをセルのインデックスに変換します。
/// @param i ビットボード上のインデックス
/// @return セルのインデックス
[[nodiscard]]
constexpr CellIndex ToCellIndex(BitBoardIndex i)
{
return static_cast<CellIndex>(63 - i);
}
/// @brief ビットボードを bool 型の配列に変換します。
/// @param bitBoard ビットボード
/// @return bool 型の配列
[[nodiscard]]
constexpr std::array<bool, 64> ToArray(BitBoard bitBoard)
{
std::array<bool, 64> results{};
for (CellIndex i = 0; i < 64; ++i)
{
results[i] = static_cast<bool>(1 & (bitBoard >> (63 - i)));
}
return results;
}
/// @brief 着手の情報
struct Move
{
/// @brief 着手位置
BitBoardIndex pos;
/// @brief 返る石
BitBoard flip;
/// @brief 着手位置をセルのインデックスで返します。
/// @return 着手位置(セルのインデックス)
CellIndex asCellIndex() const
{
return ToCellIndex(pos);
}
/// @brief 着手位置を符号で返します。
/// @return 着手位置の符号
String asLabel() const
{
return{ char32('h' - (pos % 8)), char32('8' - (pos / 8)) };
}
};
/// @brief ビットボード
class Board
{
public:
/// @brief スコアの絶対値の最大値
static constexpr int32 MaxScore = 64;
/// @brief 局面を初期化します。
void reset()
{
m_player = 0x0000000810000000ULL;
m_opponent = 0x0000001008000000ULL;
}
/// @brief 着手します。
/// @param move 着手情報
void move(Move move)
{
m_player ^= move.flip;
m_opponent ^= move.flip;
m_player ^= (1ULL << move.pos);
std::swap(m_player, m_opponent);
}
/// @brief 着手を取り消します。
/// @param move 取り消す着手情報
void undo(Move move)
{
std::swap(m_player, m_opponent);
m_player ^= (1ULL << move.pos);
m_player ^= move.flip;
m_opponent ^= move.flip;
}
/// @brief ある着手を行った場合の着手情報を返します。
/// @param move 着手位置
/// @return 着手情報
Move makeMove(BitBoardIndex pos) const
{
constexpr int32 Shifts[8] = { 1, -1, 8, -8, 7, -7, 9, -9 };
constexpr uint64 Masks[4] = { 0x7E7E7E7E7E7E7E7EULL, 0x00FFFFFFFFFFFF00ULL, 0x007E7E7E7E7E7E00ULL, 0x007E7E7E7E7E7E00ULL };
const uint64 x = (1ULL << pos);
Move move{ .pos = pos, .flip = 0ULL };
// 縦横斜めの8方向それぞれ別に計算する
for (int32 i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
move.flip |= GetFlipPart(m_player, m_opponent, Shifts[i], Masks[i / 2], x);
}
return move;
}
/// @brief 手番を入れ替えます。
void pass()
{
std::swap(m_player, m_opponent);
}
/// @brief マスの重みを使った評価で最終石差を推測します(終局していないときに使います)。
/// @return 評価値
int32 evaluate() const
{
constexpr int32 CellWeightScores[10] = { 2714, 147, 69, -18, -577, -186, -153, -379, -122, -169 };
constexpr uint64 CellWeightMasks[10] = { 0x8100000000000081ULL, 0x4281000000008142ULL, 0x2400810000810024ULL, 0x1800008181000018ULL, 0x0042000000004200ULL,
0x0024420000422400ULL, 0x0018004242001800ULL, 0x0000240000240000ULL, 0x0000182424180000ULL, 0x0000001818000000ULL };
int32 result = 0;
for (int32 i = 0; i < 10; ++i) // 盤面を10種類のマスに分けてそれぞれのマスに重みをつけたので、1種類ずつ計算
{
result += CellWeightScores[i] * (pop_count_ull(m_player & CellWeightMasks[i]) - pop_count_ull(m_opponent & CellWeightMasks[i]));
}
result += (result > 0 ? 128 : (result < 0 ? -128 : 0));
result /= 256; // 最終石差の 256 倍を学習データにしたので、256 で割って実際の最終石差の情報にする
return Max(-MaxScore, Min(MaxScore, result)); // -64 から +64 までの範囲に収める
}
/// @brief 現在の手番のビットボードを返します。
/// @return 現在の手番のビットボード
[[nodiscard]]
BitBoard getPlayerBitBoard() const
{
return m_player;
}
/// @brief 現在の手番でないほうのビットボードを返します。
/// @return 現在の手番でないほうのビットボード
[[nodiscard]]
BitBoard getOpponentBitBoard() const
{
return m_opponent;
}
/// @brief 現在の手番の合法手のビットボードで返します。
/// @return 現在の手番の合法手のビットボード
[[nodiscard]]
BitBoard getLegalBitBoard() const
{
constexpr int32 Shifts[8] = { 1, -1, 8, -8, 7, -7, 9, -9 };
constexpr uint64 Masks[4] = { 0x7E7E7E7E7E7E7E7EULL, 0x00FFFFFFFFFFFF00ULL, 0x007E7E7E7E7E7E00ULL, 0x007E7E7E7E7E7E00ULL };
BitBoard result = 0ULL;
// 縦横斜めの8方向それぞれ別に計算する
for (int32 i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
result |= GetLegalPart(m_player, m_opponent, Shifts[i], Masks[i / 2]);
}
return (result & ~(m_player | m_opponent)); // 空きマスでマスクして返す
}
/// @brief 現在の手番の得点を返します。
/// @return 現在の手番の得点
[[nodiscard]]
int32 getPlayerScore() const
{
return pop_count_ull(m_player);
}
/// @brief 現在の手番でないほうの得点を返します。
/// @return 現在の手番でないほうの得点
[[nodiscard]]
int32 getOpponentScore() const
{
return pop_count_ull(m_opponent);
}
[[nodiscard]]
int32 getScore() const
{
const int32 p = getPlayerScore();
const int32 o = getOpponentScore();
const int32 v = (64 - p - o);
return ((p > o) ? (p - o + v) : (p - o - v));
}
/// @brief 64 ビット整数の 1 のビットの個数を数えます。
/// @param x 整数
/// @return 1 のビットの個数
static constexpr int32 pop_count_ull(uint64 x)
{
x = x - ((x >> 1) & 0x5555555555555555ULL);
x = (x & 0x3333333333333333ULL) + ((x >> 2) & 0x3333333333333333ULL);
x = (x + (x >> 4)) & 0x0F0F0F0F0F0F0F0FULL;
x = (x * 0x0101010101010101ULL) >> 56;
return static_cast<int32>(x);
}
private:
// その盤面から打つ手番
BitBoard m_player = 0;
// その盤面で打たない手番
BitBoard m_opponent = 0;
// 負のシフトと正のシフトを同一に扱う関数
static constexpr uint64 EnhancedShift(uint64 a, int32 b)
{
return ((b >= 0) ? (a << b) : (a >> (-b)));
}
// 1 方向について合法手を求める
static constexpr uint64 GetLegalPart(BitBoard player, BitBoard opponent, int32 shift, uint64 mask)
{
uint64 o = (opponent & mask);
uint64 l = o & EnhancedShift(player, shift);
for (int32 i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
l |= o & EnhancedShift(l, shift);
}
return EnhancedShift(l, shift);
}
// 1 方向について着手 b によって返る石を求める
static constexpr uint64 GetFlipPart(BitBoard player, BitBoard opponent, int32 shift, uint64 mask, uint64 x)
{
uint64 o = (opponent & mask);
uint64 f = (EnhancedShift(x, shift) & o);
uint64 nf = 0ULL;
bool flipped = false;
for (int32 i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
nf = EnhancedShift(f, shift);
if (nf & player)
{
flipped = true;
break;
}
f |= (nf & o);
}
if (not flipped)
{
f = 0ULL;
}
return f;
}
};
/// @brief ゲーム情報
class Game
{
public:
/// @brief AI の計算結果
struct AI_Result
{
/// @brief 選んだ手
BitBoardIndex pos;
/// @brief AI 目線での評価値(最終石差)
int32 value;
};
Game()
{
reset();
}
~Game()
{
AbortTask(m_task);
}
void setAIDepth(int32 depth)
{
m_depth = depth;
}
/// @brief ゲームを初期化します。
void reset()
{
AbortTask(m_task);
m_board.reset();
m_activeColor = OthelloAI::Color::Black;
m_gameOver = false;
m_history.clear();
}
/// @brief 着手します。
/// @param pos 着手位置
/// @return 着手情報
Move move(BitBoardIndex pos)
{
const Move move = m_board.makeMove(pos);
m_history.emplace_back(m_activeColor, move);
m_board.move(move);
m_activeColor = ~m_activeColor;
// 合法手が無い場合は
if (m_board.getLegalBitBoard() == 0ULL)
{
// パスして手番を変更する
m_board.pass();
m_activeColor = ~m_activeColor;
// それでも合法手が無い場合は
if (m_board.getLegalBitBoard() == 0ULL)
{
// 終局
m_gameOver = true;
}
}
return move;
}
/// @brief AI に現在の手番で最適な着手位置を非同期で計算してもらいます。
/// @return 計算結果。計算途中の場合は none
[[nodiscard]]
Optional<AI_Result> calculateAsync() const
{
// AI スレッドが未開始の場合は
if (not m_task.isValid())
{
// AI スレッドを開始する
m_task = Async(AITask, m_board, m_depth);
}
// AI スレッドが計算完了した場合は
if (m_task.isReady())
{
return m_task.get();
}
return none;
}
/// @brief AI に現在の手番で最適な着手位置を計算してもらいます。
/// @return 計算結果
AI_Result calculate() const
{
return AITask(m_board, m_depth);
}
/// @brief 黒の石の配置を返します。
/// @return 黒の石の配置
[[nodiscard]]
std::array<bool, 64> getBlackDisks() const
{
return ToArray((m_activeColor == OthelloAI::Color::Black) ? m_board.getPlayerBitBoard() : m_board.getOpponentBitBoard());
}
/// @brief 白の石の配置を返します。
/// @return 白の石の配置
[[nodiscard]]
std::array<bool, 64> getWhiteDisks() const
{
return ToArray((m_activeColor == OthelloAI::Color::Black) ? m_board.getOpponentBitBoard() : m_board.getPlayerBitBoard());
}
/// @brief 合法手の配置を返します。
/// @return 合法手の配置
[[nodiscard]]
std::array<bool, 64> getLegals() const
{
return ToArray(m_board.getLegalBitBoard());
}
/// @brief 現在アクティブな色を返します。
/// @return 現在アクティブな色
[[nodiscard]]
OthelloAI::Color getActiveColor() const
{
return m_activeColor;
}
/// @brief 終局しているかを返します。
/// @return 終局している場合は true, それ以外の場合は false
[[nodiscard]]
bool isOver() const
{
return m_gameOver;
}
/// @brief 黒の得点を返します。
/// @return 黒の得点
[[nodiscard]]
int32 getBlackScore() const
{
return ((m_activeColor == OthelloAI::Color::Black) ? m_board.getPlayerScore() : m_board.getOpponentScore());
}
/// @brief 白の得点を返します。
/// @return 白の得点
[[nodiscard]]
int32 getWhiteScore() const
{
return ((m_activeColor == OthelloAI::Color::Black) ? m_board.getOpponentScore() : m_board.getPlayerScore());
}
/// @brief 着手の履歴を返します。
/// @return 着手の履歴
[[nodiscard]]
const Array<std::pair<OthelloAI::Color, OthelloAI::Move>>& getHistory() const
{
return m_history;
}
/// @brief ビットボードを返します。
/// @return ビットボード
[[nodiscard]]
const Board& getBoard() const
{
return m_board;
}
private:
// ビットボード
Board m_board;
// 現在アクティブな色
OthelloAI::Color m_activeColor = OthelloAI::Color::Black;
// 着手履歴
Array<std::pair<OthelloAI::Color, OthelloAI::Move>> m_history;
// 終局しているか
bool m_gameOver = false;
// 先読みの手数
int32 m_depth = 5;
// AI の非同期タスク
mutable AsyncTask<AI_Result> m_task;
// AI 非同期タスクの中断フラグ
inline static std::atomic<bool> m_abort = false;
// 2 進数として数値を見て右端からいくつ 0 が連続しているか: Number of Training Zero
static uint_fast8_t ntz(uint64* x)
{
return static_cast<uint_fast8_t>(Board::pop_count_ull((~(*x)) & ((*x) - 1)));
}
// 立っているビットを走査するときに for 文で使うと便利
static uint_fast8_t first_bit(uint64* x)
{
return ntz(x);
}
// 立っているビットを走査するときに for 文で使うと便利
static uint_fast8_t next_bit(uint64* x)
{
*x &= *x - 1; // 最右の立っているビットをオフにする
return ntz(x);
}
// AI の根幹部分。Nega-Alpha 法
static int32 NegaAlpha(Board board, int32 depth, int32 alpha, int32 beta, bool passed)
{
if (m_abort) // 強制終了
{
return -Board::MaxScore;
}
if (depth <= 0) // 探索終了
{
return board.evaluate();
}
BitBoard legal = board.getLegalBitBoard(); // 合法手生成
if (legal == 0ULL) // パスの場合
{
if (passed) // 2回パスしたら終局
{
return board.getScore();
}
board.pass();
return -NegaAlpha(board, depth, -beta, -alpha, true); // 手番を入れ替えてもう一度探索
}
Move move;
for (BitBoardIndex cell = first_bit(&legal); legal; cell = next_bit(&legal)) // 合法手を走査
{
move = board.makeMove(cell); // 返る石を計算
board.move(move); // 着手する
alpha = Max(alpha, -NegaAlpha(board, depth - 1, -beta, -alpha, false)); // 次の手番の探索
board.undo(move); // 着手を取り消す
if (beta <= alpha) // 途中で枝刈りできる場合はする
{
break;
}
}
return alpha; // 求めた評価値を返す
}
// NegaAlpha は評価値を求めることしかできないので、この関数で実際に打つ手を選ぶ。
static AI_Result AITask(Board board, int32 depth)
{
AI_Result result = { 0, (-Board::MaxScore - 1) };
BitBoard legal = board.getLegalBitBoard(); // 合法手生成
int32 value = 0;
Move move;
// 各合法手について
for (BitBoardIndex pos = first_bit(&legal); legal; pos = next_bit(&legal))
{
move = board.makeMove(pos); // 返る石を求める
board.move(move); // 着手
value = -NegaAlpha(board, depth - 1, -Board::MaxScore, -result.value, false); // 評価値を求める
board.undo(move); // 着手を取り消す
if (result.value < value) // これまで見た評価値よりも良い評価値なら値を更新
{
result = { pos, value };
}
}
return result;
}
// 非同期タスクを中断する
static void AbortTask(AsyncTask<AI_Result>& task)
{
if (task.isValid())
{
m_abort = true;
task.get();
m_abort = false;
}
}
};
}
////////////////////////////////
//
// UI
//
////////////////////////////////
/// @brief ボードのサイズ
constexpr double BoardSize = 400;
/// @brief セルの大きさ
constexpr double CellSize = (BoardSize / 8);
/// @brief 黒石の色
constexpr ColorF BlackDiskColor{ 0.11 };
/// @brief 白石の色
constexpr ColorF WhiteDiskColor{ 0.98 };
/// @brief セルのインデックスを座標に変換します。
/// @param i セルのインデックス
/// @return セルの座標
[[nodiscard]]
constexpr Vec2 ToVec2(OthelloAI::CellIndex i)
{
return (Vec2{ (i % 8), (i / 8) } * CellSize + CellSize * Vec2{ 0.5, 0.5 });
}
/// @brief 盤面を描画します。
/// @param game ゲーム
/// @param pos ボードの左上の位置
/// @param labelFont ラベル用フォント
/// @param t アニメーション [0.0, 1.0]
void DrawBoard(const OthelloAI::Game& game, const Vec2& pos, const Font& labelFont, double t)
{
constexpr double GridThickness = 2;
constexpr double GridDotRadius = (CellSize * 0.1);
constexpr double DiskRadius = (CellSize * 0.4);
constexpr ColorF GridColor{ 0.2 };
constexpr ColorF DiskShadowColor{ 0.0, 0.5 };
// 行・列ラベルを描画する
for (int32 i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
labelFont(i + 1).draw(15, Arg::center((pos.x - 20), (pos.y + CellSize * i + CellSize / 2)), GridColor);
labelFont(char32(U'a' + i)).draw(15, Arg::center((pos.x + CellSize * i + CellSize / 2), (pos.y - 20 - 2)), GridColor);
}
// グリッドを描画する
for (int32 i = 0; i <= 8; ++i)
{
Line{ pos.x + CellSize * i, pos.y, pos.x + CellSize * i, pos.y + BoardSize }.draw(GridThickness, GridColor);
Line{ pos.x, pos.y + CellSize * i, pos.x + BoardSize, pos.y + CellSize * i }.draw(GridThickness, GridColor);
}
// グリッド上の丸い模様を描画する
{
Circle{ (pos.x + 2 * CellSize), (pos.y + 2 * CellSize), GridDotRadius }.draw(GridColor);
Circle{ (pos.x + 2 * CellSize), (pos.y + 6 * CellSize), GridDotRadius }.draw(GridColor);
Circle{ (pos.x + 6 * CellSize), (pos.y + 2 * CellSize), GridDotRadius }.draw(GridColor);
Circle{ (pos.x + 6 * CellSize), (pos.y + 6 * CellSize), GridDotRadius }.draw(GridColor);
}
// 石を描画する
{
const std::array<bool, 64> balckDisks = game.getBlackDisks();
const std::array<bool, 64> whiteDisks = game.getWhiteDisks();
std::array<bool, 64> flips{};
if (game.getHistory())
{
flips = OthelloAI::ToArray(game.getHistory().back().second.flip);
}
t = EaseInOutCirc(t);
for (OthelloAI::CellIndex i = 0; i < 64; ++i)
{
const Vec2 center = pos + ToVec2(i);
const Circle disk{ center, DiskRadius };
if (flips[i] && (t < 1.0))
{
const Transformer2D tr{ Mat3x2::Scale((t < 0.5) ? (0.5 - t) * 2 : (t - 0.5) * 2, 1.0, center) };
disk.drawShadow(Vec2{ 0, 2 }, 7, 2, DiskShadowColor);
if (balckDisks[i])
{
if (t < 0.5)
{
disk.draw(WhiteDiskColor);
}
else
{
disk.draw(BlackDiskColor);
}
}
else if (whiteDisks[i])
{
if (t < 0.5)
{
disk.draw(BlackDiskColor);
}
else
{
disk.draw(WhiteDiskColor);
}
}
}
else
{
if (balckDisks[i])
{
disk.drawShadow(Vec2{ 0, 2 }, 7, 2, DiskShadowColor).draw(BlackDiskColor);
}
else if (whiteDisks[i])
{
disk.drawShadow(Vec2{ 0, 2 }, 7, 2, DiskShadowColor).draw(WhiteDiskColor);
}
}
}
}
}
/// @brief 人間の手番でセルをクリックして着手します。
/// @param game ゲーム
/// @param pos ボードの左上の位置
/// @return 着手した場合はビットボード上のインデックス、それ以外の場合は none
Optional<OthelloAI::BitBoardIndex> UpdateManually(OthelloAI::Game& game, const Vec2& pos)
{
// 現在の合法手
const std::array<bool, 64> legals = game.getLegals();
for (OthelloAI::CellIndex i = 0; i < 64; ++i)
{
// 合法手でなければスキップ
if (not legals[i])
{
continue;
}
const RectF cell{ Arg::center = (pos + ToVec2(i)), CellSize };
cell.drawFrame(CellSize * 0.15, 0, ColorF{ 1.0, 0.4 });
// 合法手をマウスオーバーしていたら
if (cell.mouseOver())
{
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
cell.draw(ColorF{ 1.0, 0.5 });
// その合法手で返すことのできる石
const std::array<bool, 64> flips = OthelloAI::ToArray(game.getBoard().makeMove(OthelloAI::ToBitBoardIndex(i)).flip);
for (OthelloAI::CellIndex k = 0; k < 64; ++k)
{
if (flips[k])
{
RectF{ Arg::center = (pos + ToVec2(k)), CellSize }
.draw(ColorF{ Palette::Orange, 0.6 });
}
}
if (cell.leftClicked())
{
return OthelloAI::ToBitBoardIndex(i);
}
}
}
return none;
}
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.15, 0.6, 0.45 });
constexpr Vec2 BoardOffset{ 40, 40 };
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
// 手番開始時のクールタイム
constexpr Duration CoolTime = 0.5s;
// ゲームの情報
OthelloAI::Game game;
// AI の先読み手数(先読み手数が大きいと強くなるが、計算時間が長くなる。1 ~ 9 が目安)
game.setAIDepth(5);
// AI 視点での評価値
int32 value = 0;
// 人間プレイヤーの色
OthelloAI::Color humanColor = OthelloAI::Color::Black;
// 着手からの経過時間測定
Stopwatch stopwatch{ StartImmediately::Yes };
while (System::Update())
{
////////////////////////////////
//
// 状態の更新
//
////////////////////////////////
{
// 終局していなければ
if (not game.isOver() && (CoolTime <= stopwatch))
{
if (game.getActiveColor() == humanColor) // 人間の手番
{
// 人間による着手
if (const auto result = UpdateManually(game, BoardOffset))
{
const auto record = game.move(*result);
stopwatch.restart();
}
}
else // AI の手番
{
// 非同期で計算
if (const auto result = game.calculateAsync())
{
const auto record = game.move(result->pos);
value = result->value;
stopwatch.restart();
}
}
}
}
////////////////////////////////
//
// 描画
//
////////////////////////////////
{
// ボード
DrawBoard(game, BoardOffset, font, Min(1.0, (stopwatch.elapsed() / (CoolTime * 0.6))));
// 対局開始ボタン
{
Optional<OthelloAI::Color> reset;
if (SimpleGUI::Button(U"\U000F012F 先手 (黒) で対局開始", Vec2{ 470, 40 }))
{
reset = OthelloAI::Color::Black;
}
if (SimpleGUI::Button(U"\U000F0130 後手 (白) で対局開始", Vec2{ 470, 80 }))
{
reset = OthelloAI::Color::White;
}
if (reset)
{
game.reset();
value = 0;
humanColor = *reset;
}
}
// 手番の表示
if (not game.isOver())
{
font(U"{}番({}の手番)"_fmt(
((game.getActiveColor() == OthelloAI::Color::Black) ? U'黒' : U'白'),
((game.getActiveColor() == humanColor) ? U"あなた" : U"AI ")
)).draw(20, Vec2{ 470, 140 });
}
else
{
font(U"終局").draw(20, Vec2{ 470, 140 });
}
// 得点の表示
{
Circle{ 480, 190, 12 }.draw(BlackDiskColor);
Circle{ 600, 190, 12 }.draw(WhiteDiskColor);
Line{ 540, 178, 540, 202 }.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
font(game.getBlackScore()).draw(20, Arg::leftCenter(500, 190));
font(game.getWhiteScore()).draw(20, Arg::rightCenter(580, 190));
}
font(U"AI 視点の評価値: {}"_fmt(value)).draw(20, Vec2{ 470, 220 });
}
}
}
4.8 シンプルな 3D 描画¶

商業エンジンほどの高度な機能はありませんが、短いコードで 3D 描画を行うことができます。次のサンプルは Siv3D の 3D 描画機能を使った最もシンプルな例です。
現在開発中のアップデート Siv3D v0.8 では 3D 描画機能が強化される予定です。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
// ウインドウとシーンを 1280x720 にリサイズ
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
// 背景色 (リニアレンダリング用なので removeSRGBCurve() で sRGB カーブを除去)
const ColorF backgroundColor = ColorF{ 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 }.removeSRGBCurve();
// UV チェック用テクスチャ (ミップマップ使用。リニアレンダリング時に正しく扱われるよう、sRGB テクスチャであると明示)
const Texture uvChecker{ U"example/texture/uv.png", TextureDesc::MippedSRGB };
// 3D シーンを描く、マルチサンプリング対応レンダーテクスチャ
// リニア色空間のレンダリング用に TextureFormat::R8G8B8A8_Unorm_SRGB
// 奥行きの比較のための深度バッファも使うので HasDepth::Yes
// マルチサンプル・レンダーテクスチャなので、描画内容を使う前に resolve() が必要
const MSRenderTexture renderTexture{ Scene::Size(), TextureFormat::R8G8B8A8_Unorm_SRGB, HasDepth::Yes };
// 3D シーンのデバッグ用カメラ
// 縦方向の視野角 30°, カメラの位置 (10, 16, -32)
// 前後移動: [W][S], 左右移動: [A][D], 上下移動: [E][X], 注視点移動: アローキー, 加速: [Shift][Ctrl]
DebugCamera3D camera{ renderTexture.size(), 30_deg, Vec3{ 10, 16, -32 } };
while (System::Update())
{
// デバッグカメラの更新 (カメラの移動スピード: 2.0)
camera.update(2.0);
// 3D シーンにカメラを設定
Graphics3D::SetCameraTransform(camera);
// 3D 描画
{
// renderTexture を背景色で塗りつぶし、
// renderTexture を 3D 描画のレンダーターゲットに
const ScopedRenderTarget3D target{ renderTexture.clear(backgroundColor) };
// 床を描画
Plane{ 64 }.draw(uvChecker);
// ボックスを描画
Box{ -8,2,0,4 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.8, 0.6, 0.4 }.removeSRGBCurve());
// 球を描画
Sphere{ 0,2,0,2 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.4, 0.8, 0.6 }.removeSRGBCurve());
// 円柱を描画
Cylinder{ 8, 2, 0, 2, 4 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.4, 0.8 }.removeSRGBCurve());
}
// 3D シーンを 2D シーンに描画
{
// renderTexture を resolve する前に 3D 描画を実行する
Graphics3D::Flush();
// マルチサンプル・テクスチャのリゾルブ
renderTexture.resolve();
// リニアレンダリングされた renderTexture をシーンに転送
Shader::LinearToScreen(renderTexture);
}
}
}