11. シェーダ応用¶
11.1 ディゾルブシェーダの準備¶
Perlin ノイズテクスチャを使って、画像が徐々に侵食されて消えていくような効果を実現するディゾルブシェーダを作成します。
まずはシェーダを使わずに、原理を理解するためのプログラムを作成します。
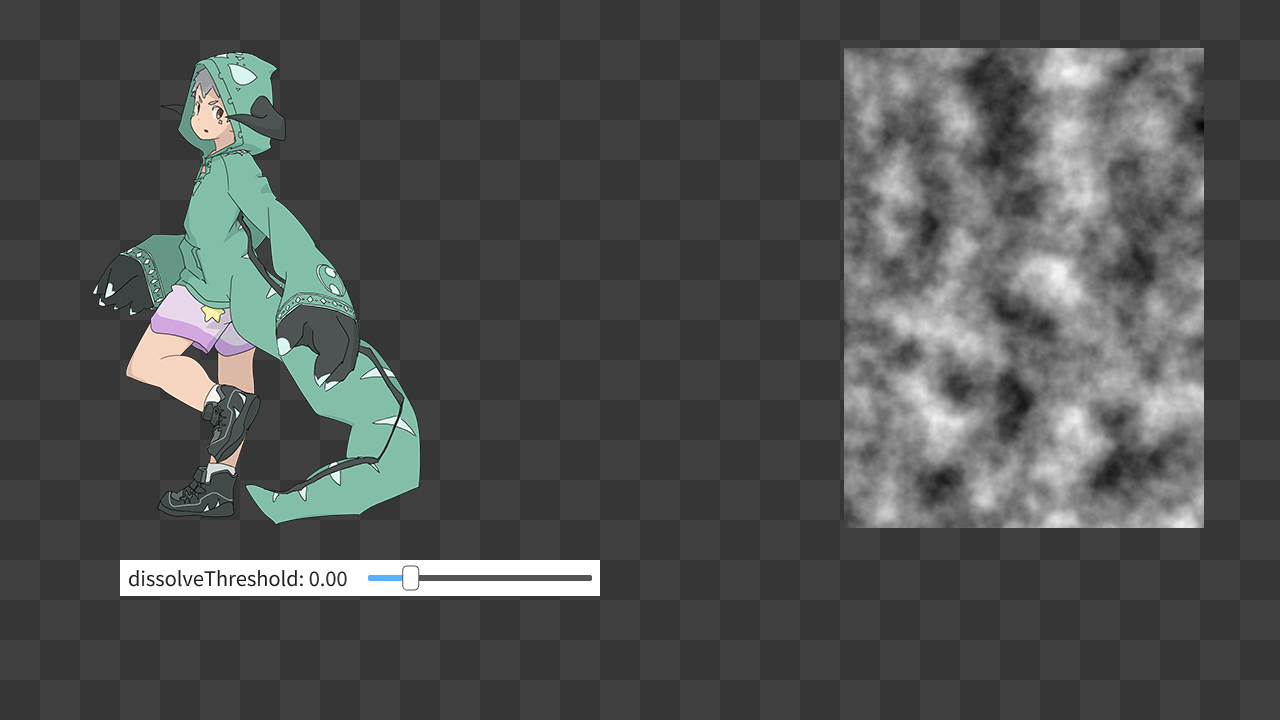
左が Siv3D のマスコットキャラクター「Siv3D くん」のテクスチャ、右が Perlin ノイズテクスチャです。
ここではまだカスタムシェーダを使っていないので何も起こりません。
このあと、Siv3D くんのテクスチャを描く際に Perlin ノイズテクスチャを参照し、その値が閾値より小さい場合は描画しない(完全に透過する)ようにすることで、閾値が大きくなるにつれて Siv3D くんが侵食されるように消えていく効果を実現します。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void DrawBackground()
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < (Scene::Height() / 40); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / 40); ++x)
{
if (IsEven(x + y))
{
RectF{ (x * 40), (y * 40), 40 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.25 });
}
}
}
}
/// @brief 指定されたサイズのノイズ画像を生成します。
/// @param size 画像のサイズ
/// @return 生成したノイズ画像
Image GenerateNoiseImage(const Size& size)
{
Image image{ size };
PerlinNoise noise{ RandomUint32() };
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
const double t = noise.octave2D0_1((x / 64.0), (y / 64.0), 5);
image[y][x] = ColorF{ t };
}
}
return image;
}
struct DissolveConstants
{
float dissolveThreshold;
};
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.21 });
const Texture texture{ U"example/siv3d-kun.png", TextureDesc::Mipped };
Texture noiseTexture{ GenerateNoiseImage(texture.size()), TextureDesc::Mipped };
// 侵食の閾値
double dissolveThreshold = 0.0;
while (System::Update())
{
// 背景と比較用のテクスチャ描画
{
DrawBackground();
texture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.2, 0.4));
noiseTexture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.8, 0.4));
}
// 侵食されるテクスチャ描画
{
}
// GUI
{
SimpleGUI::Slider(U"dissolveThreshold: {:.2f}"_fmt(dissolveThreshold), dissolveThreshold, -0.2, 1.0, Vec2{ 120, 560 }, 240, 240);
}
}
}
11.2 ディゾルブシェーダの適用¶
ディゾルブを実現するためのシェーダファイルを作成します。
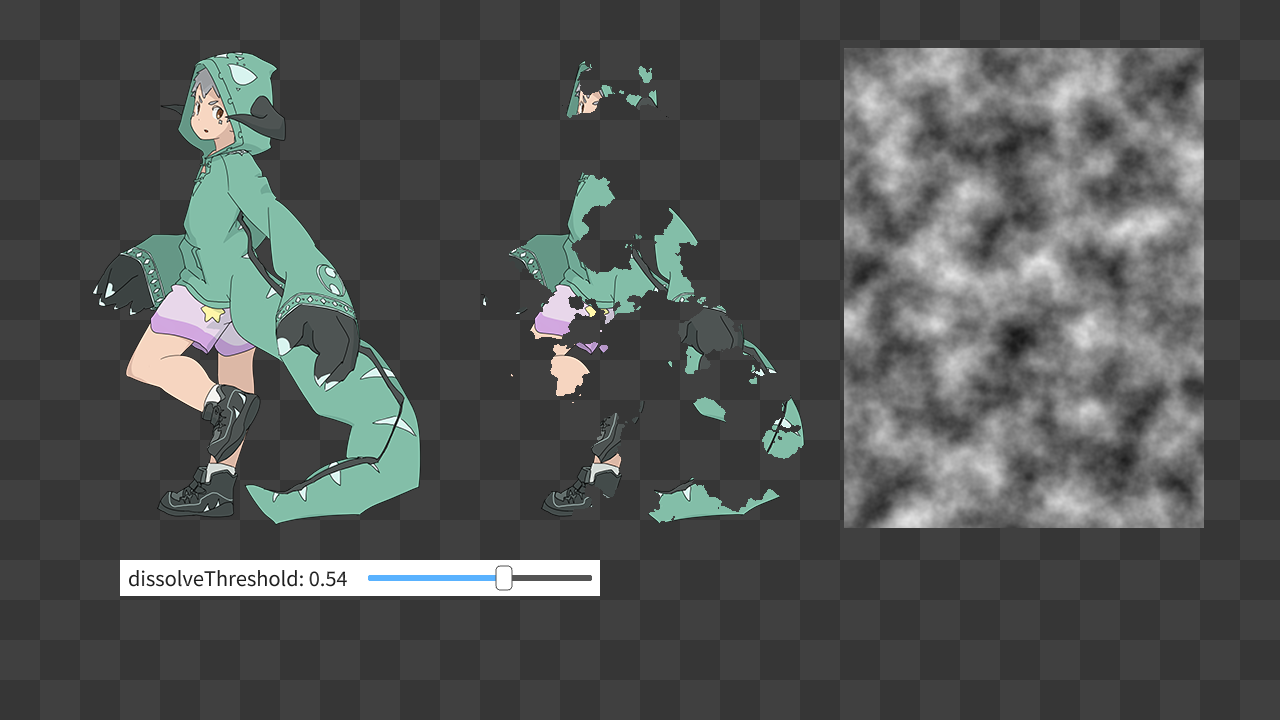
R 成分と B 成分の入れ替えに使ったシェーダファイル example/shader/hlsl/rgb_to_bgr.hlsl または example/shader/glsl/rgb_to_bgr.frag を同じフォルダ内でコピーし、それぞれ dissolve.hlsl, dissolve.frag という名前に変更しましょう。
中身を次のように書き換えます。
HLSL
//
// Textures
//
Texture2D g_texture0 : register(t0);
Texture2D g_texture1 : register(t1);
SamplerState g_sampler0 : register(s0);
SamplerState g_sampler1 : register(s1);
namespace s3d
{
//
// VS Output / PS Input
//
struct PSInput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR0;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
cbuffer PSConstants2D : register(b0)
{
float4 g_colorAdd;
float4 g_sdfParam;
float4 g_sdfOutlineColor;
float4 g_sdfShadowColor;
float4 g_internal;
}
cbuffer DissolveConstants : register(b1)
{
float g_dissolveThreshold;
}
float4 PS(s3d::PSInput input) : SV_TARGET
{
float4 texColor = g_texture0.Sample(g_sampler0, input.uv);
float value = g_texture1.Sample(g_sampler1, input.uv).r;
if (value < g_dissolveThreshold)
{
texColor.a = 0.0;
}
return (texColor * input.color) + g_colorAdd;
}
GLSL
# version 410
//
// Textures
//
uniform sampler2D Texture0;
uniform sampler2D Texture1;
//
// PSInput
//
layout(location = 0) in vec4 Color;
layout(location = 1) in vec2 UV;
//
// PSOutput
//
layout(location = 0) out vec4 FragColor;
//
// Constant Buffer
//
layout(std140) uniform PSConstants2D
{
vec4 g_colorAdd;
vec4 g_sdfParam;
vec4 g_sdfOutlineColor;
vec4 g_sdfShadowColor;
vec4 g_internal;
};
layout(std140) uniform DissolveConstants
{
float g_dissolveThreshold;
};
//
// Functions
//
void main()
{
vec4 texColor = texture(Texture0, UV);
float value = texture(Texture1, UV).r;
if (value < g_dissolveThreshold)
{
texColor.a = 0.0;
}
FragColor = (texColor * Color) + g_colorAdd;
}
HLSL, GLSL, いずれのピクセルシェーダでも、PerlinNoise テクスチャ(テクスチャスロット 1)から読み込んだ値について、それが定数バッファ DissolveConstants の値 g_dissolveThreshold より小さければ完全に透過するようにします。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void DrawBackground()
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < (Scene::Height() / 40); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / 40); ++x)
{
if (IsEven(x + y))
{
RectF{ (x * 40), (y * 40), 40 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.25 });
}
}
}
}
/// @brief 指定されたサイズのノイズ画像を生成します。
/// @param size 画像のサイズ
/// @return 生成したノイズ画像
Image GenerateNoiseImage(const Size& size)
{
Image image{ size };
PerlinNoise noise{ RandomUint32() };
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
const double t = noise.octave2D0_1((x / 64.0), (y / 64.0), 5);
image[y][x] = ColorF{ t };
}
}
return image;
}
struct DissolveConstants
{
float dissolveThreshold;
};
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.21 });
const Texture texture{ U"example/siv3d-kun.png", TextureDesc::Mipped };
Texture noiseTexture{ GenerateNoiseImage(texture.size()), TextureDesc::Mipped };
const PixelShader ps = HLSL{ U"example/shader/hlsl/dissolve.hlsl", U"PS" } | GLSL{ U"example/shader/glsl/dissolve.frag", {{ U"PSConstants2D", 0 }, { U"DissolveConstants", 1 }} };
if (not ps)
{
throw Error{ U"Failed to load a shader file" };
}
ConstantBuffer<DissolveConstants> cb;
// 侵食の閾値
double dissolveThreshold = 0.0;
while (System::Update())
{
cb->dissolveThreshold = static_cast<float>(dissolveThreshold);
// 背景と比較用のテクスチャ描画
{
DrawBackground();
texture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.2, 0.4));
noiseTexture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.8, 0.4));
}
// 侵食されるテクスチャ描画
{
Graphics2D::SetPSConstantBuffer(1, cb);
Graphics2D::SetPSTexture(1, noiseTexture);
const ScopedCustomShader2D shader{ ps };
texture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.5, 0.4));
}
// GUI
{
SimpleGUI::Slider(U"dissolveThreshold: {:.2f}"_fmt(dissolveThreshold), dissolveThreshold, -0.2, 1.0, Vec2{ 120, 560 }, 240, 240);
}
}
}
Graphics2D::SetPSTexture(1, noiseTexture); によって、PerlinNoise テクスチャをシェーダの追加のテクスチャスロット 1 に設定します。
11.3 ディゾルブシェーダの発展¶
シェーダプログラムをさらに発展させると、炎によって侵食されるような効果を付加できます。
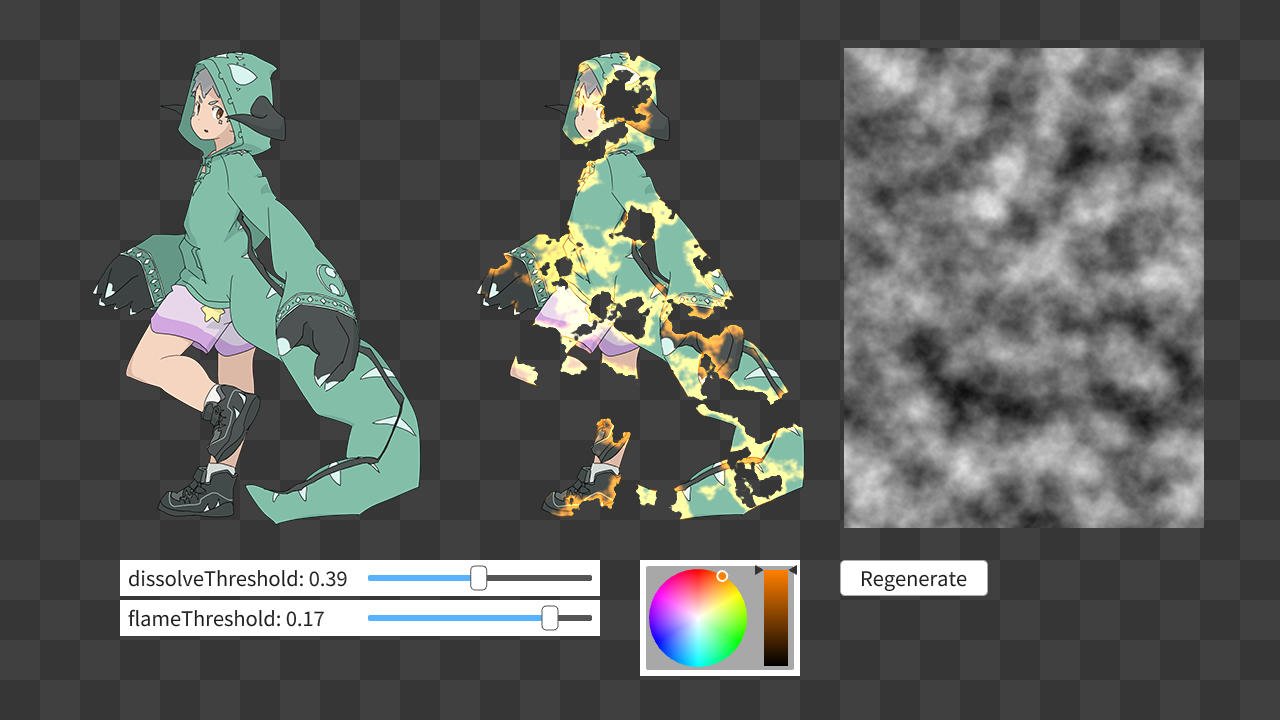
HLSL
//
// Textures
//
Texture2D g_texture0 : register(t0);
Texture2D g_texture1 : register(t1);
SamplerState g_sampler0 : register(s0);
SamplerState g_sampler1 : register(s1);
namespace s3d
{
//
// VS Output / PS Input
//
struct PSInput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR0;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
cbuffer PSConstants2D : register(b0)
{
float4 g_colorAdd;
float4 g_sdfParam;
float4 g_sdfOutlineColor;
float4 g_sdfShadowColor;
float4 g_internal;
}
cbuffer DissolveConstants : register(b1)
{
float g_dissolveThreshold;
float g_flameThreshold;
float3 g_flameColor;
}
float4 PS(s3d::PSInput input) : SV_TARGET
{
float4 texColor = g_texture0.Sample(g_sampler0, input.uv);
float value = g_texture1.Sample(g_sampler1, input.uv).r;
float diff = (value - g_dissolveThreshold);
float burn = smoothstep(g_flameThreshold, 0.0, diff);
texColor.rgb += (burn * g_flameColor);
float dissolve = smoothstep(0.0, 0.02, diff);
texColor.a *= dissolve;
return (texColor * input.color) + g_colorAdd;
}
GLSL
# version 410
//
// Textures
//
uniform sampler2D Texture0;
uniform sampler2D Texture1;
//
// PSInput
//
layout(location = 0) in vec4 Color;
layout(location = 1) in vec2 UV;
//
// PSOutput
//
layout(location = 0) out vec4 FragColor;
//
// Constant Buffer
//
layout(std140) uniform PSConstants2D
{
vec4 g_colorAdd;
vec4 g_sdfParam;
vec4 g_sdfOutlineColor;
vec4 g_sdfShadowColor;
vec4 g_internal;
};
layout(std140) uniform DissolveConstants
{
float g_dissolveThreshold;
float g_flameThreshold;
vec3 g_flameColor;
};
//
// Functions
//
void main()
{
vec4 texColor = texture(Texture0, UV);
float value = texture(Texture1, UV).r;
float diff = (value - g_dissolveThreshold);
float burn = smoothstep(g_flameThreshold, 0.0, diff);
texColor.rgb += (burn * g_flameColor);
float dissolve = smoothstep(0.0, 0.02, diff);
texColor.a *= dissolve;
FragColor = (texColor * Color) + g_colorAdd;
}
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void DrawBackground()
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < (Scene::Height() / 40); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / 40); ++x)
{
if (IsEven(x + y))
{
RectF{ (x * 40), (y * 40), 40 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.25 });
}
}
}
}
/// @brief 指定されたサイズのノイズ画像を生成します。
/// @param size 画像のサイズ
/// @return 生成したノイズ画像
Image GenerateNoiseImage(const Size& size)
{
Image image{ size };
PerlinNoise noise{ RandomUint32() };
for (int32 y = 0; y < size.y; ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < size.x; ++x)
{
const double t = noise.octave2D0_1((x / 64.0), (y / 64.0), 5);
image[y][x] = ColorF{ t };
}
}
return image;
}
struct DissolveConstants
{
float dissolveThreshold;
float flameThreshold;
Float2 _padding; // ベクトル型の前には 16 バイトアライメントに揃えるためのパディングが必要
Float3 flameColor;
};
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.21 });
const Texture texture{ U"example/siv3d-kun.png", TextureDesc::Mipped };
Texture noiseTexture{ GenerateNoiseImage(texture.size()), TextureDesc::Mipped };
const PixelShader ps = HLSL{ U"example/shader/hlsl/dissolve.hlsl", U"PS" } | GLSL{ U"example/shader/glsl/dissolve.frag", {{ U"PSConstants2D", 0 }, { U"DissolveConstants", 1 }} };
if (not ps)
{
throw Error{ U"Failed to load a shader file" };
}
ConstantBuffer<DissolveConstants> cb;
// 侵食の閾値
double dissolveThreshold = 0.0;
// 炎の閾値
double flameThreshold = 0.1;
// 炎の色
HSV flameColor{ 30, 1.0, 1.0 };
while (System::Update())
{
cb->dissolveThreshold = static_cast<float>(dissolveThreshold);
cb->flameThreshold = static_cast<float>(flameThreshold);
cb->flameColor = flameColor.toColorF().rgb();
// 背景と比較用のテクスチャ描画
{
DrawBackground();
texture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.2, 0.4));
noiseTexture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.8, 0.4));
}
// 炎による侵食を伴うテクスチャ描画
{
Graphics2D::SetPSConstantBuffer(1, cb);
Graphics2D::SetPSTexture(1, noiseTexture);
const ScopedCustomShader2D shader{ ps };
texture.drawAt(Scene::Rect().getRelativePoint(0.5, 0.4));
}
// GUI
{
SimpleGUI::Slider(U"dissolveThreshold: {:.2f}"_fmt(dissolveThreshold), dissolveThreshold, -0.2, 1.0, Vec2{ 120, 560 }, 240, 240);
SimpleGUI::Slider(U"flameThreshold: {:.2f}"_fmt(flameThreshold), flameThreshold, 0.0, 0.2, Vec2{ 120, 600 }, 240, 240);
SimpleGUI::ColorPicker(flameColor, Vec2{ 640, 560 });
if (SimpleGUI::Button(U"Regenerate", Vec2{ 840, 560 }))
{
noiseTexture = Texture{ GenerateNoiseImage(texture.size()), TextureDesc::Mipped };
}
}
}
}
11.4 シェーダでの頂点生成¶
頂点シェーダを使った、頂点位置の特殊な制御を体験してみましょう。
通常、図形や画像を描くときの頂点座標配列は、CPU で目的の形状に沿うように計算したものを GPU に転送し、そのまま使っています。
複雑な計算で座標が決まる大量の頂点を扱う場合については、各頂点の内容の生成を完全に GPU に任せることで、CPU の負担を減らすことができます。
Siv3D の Graphics2D::DrawTriangles(n) は、頂点情報が一切設定されていない n 個の三角形を描画する関数です。それらの各頂点の座標をどこにするかや、色をどうするかは、頂点シェーダ内で頂点のインデックス ID を使いながら計算することになります。
次のコードでは、この方法の練習として 1 個の三角形を描きます。頂点位置の決定に CPU 側のプログラムは関与していません。

HLSL
namespace s3d
{
//
// VS Output
//
struct PSInput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR0;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
//
// Siv3D Functions
//
float4 Transform2D(float2 pos, float2x4 t)
{
return float4((t._13_14 + (pos.x * t._11_12) + (pos.y * t._21_22)), t._23_24);
}
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
cbuffer VSConstants2D : register(b0)
{
row_major float2x4 g_transform;
float4 g_colorMul;
}
//
// Functions
//
s3d::PSInput VS(uint id : SV_VERTEXID)
{
s3d::PSInput result;
float2 pos;
float4 color;
if (id == 0)
{
pos = float2(300, 300);
color = float4(1, 0, 0, 1); // red
}
else if (id == 1)
{
pos = float2(500, 500);
color = float4(0, 1, 0, 1); // green
}
else if (id == 2)
{
pos = float2(300, 500);
color = float4(0, 0, 1, 1); // blue
}
result.position = s3d::Transform2D(pos, g_transform);
result.color = color;
result.uv = float2(0, 0);
return result;
}
GLSL
# version 410
//
// VS Input (nothing)
//
//
// VS Output
//
layout(location = 0) out vec4 Color;
layout(location = 1) out vec2 UV;
out gl_PerVertex
{
vec4 gl_Position;
};
//
// Siv3D Functions
//
vec4 s3d_Transform2D(const vec2 pos, const vec4 t[2])
{
return vec4(t[0].zw + (pos.x * t[0].xy) + (pos.y * t[1].xy), t[1].zw);
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
layout(std140) uniform VSConstants2D
{
vec4 g_transform[2];
vec4 g_colorMul;
};
//
// Functions
//
void main()
{
vec2 pos;
vec4 color;
uint id = gl_VertexID;
if (id == 0)
{
pos = vec2(300, 300);
color = vec4(1, 0, 0, 1); // red
}
else if (id == 1)
{
pos = vec2(500, 500);
color = vec4(0, 1, 0, 1); // green
}
else if (id == 2)
{
pos = vec2(300, 500);
color = vec4(0, 0, 1, 1); // blue
}
gl_Position = s3d_Transform2D(pos, g_transform);
Color = color;
UV = vec2(0, 0);
}
三角形を 1 個描く場合、頂点インデックス 0, 1, 2 の 3 つの頂点の座標と色を計算します。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void DrawBackground()
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < (Scene::Height() / 40); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / 40); ++x)
{
if (IsEven(x + y))
{
RectF{ (x * 40), (y * 40), 40 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.85 });
}
}
}
}
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.80 });
const VertexShader vs
= HLSL{ U"example/shader/hlsl/wave.hlsl" }
| GLSL{ U"example/shader/glsl/wave.vert", { { U"VSConstants2D", 0 } } };
if (not vs)
{
throw Error{ U"Failed to load a shader file" };
}
ConstantBuffer<float> cb;
bool showWireframe = false;
while (System::Update())
{
cb = static_cast<float>(Scene::Time());
DrawBackground();
{
Graphics2D::SetVSConstantBuffer(1, cb);
const ScopedRenderStates2D states{ showWireframe ? RasterizerState::WireframeCullNone : RasterizerState::Default2D };
const ScopedCustomShader2D shader{ vs };
// 頂点情報の無い三角形を 1 個描画する
// (頂点情報は頂点シェーダで設定する)
Graphics2D::DrawTriangles(1);
}
SimpleGUI::CheckBox(showWireframe, U"Wireframe", Vec2{ 60, 60 });
}
}
11.5 シェーダでの頂点生成の応用 ①¶
GPU での頂点情報生成は、頂点数が少ない場合は負荷分散の効果が薄いですが、頂点数が多い場合には CPU の負担を大きく減らすことができます。
次のコードは、時間の経過とともに波打つ図形の座標を頂点シェーダで生成して描画します。頂点位置の決定に CPU 側のプログラムは関与していません。
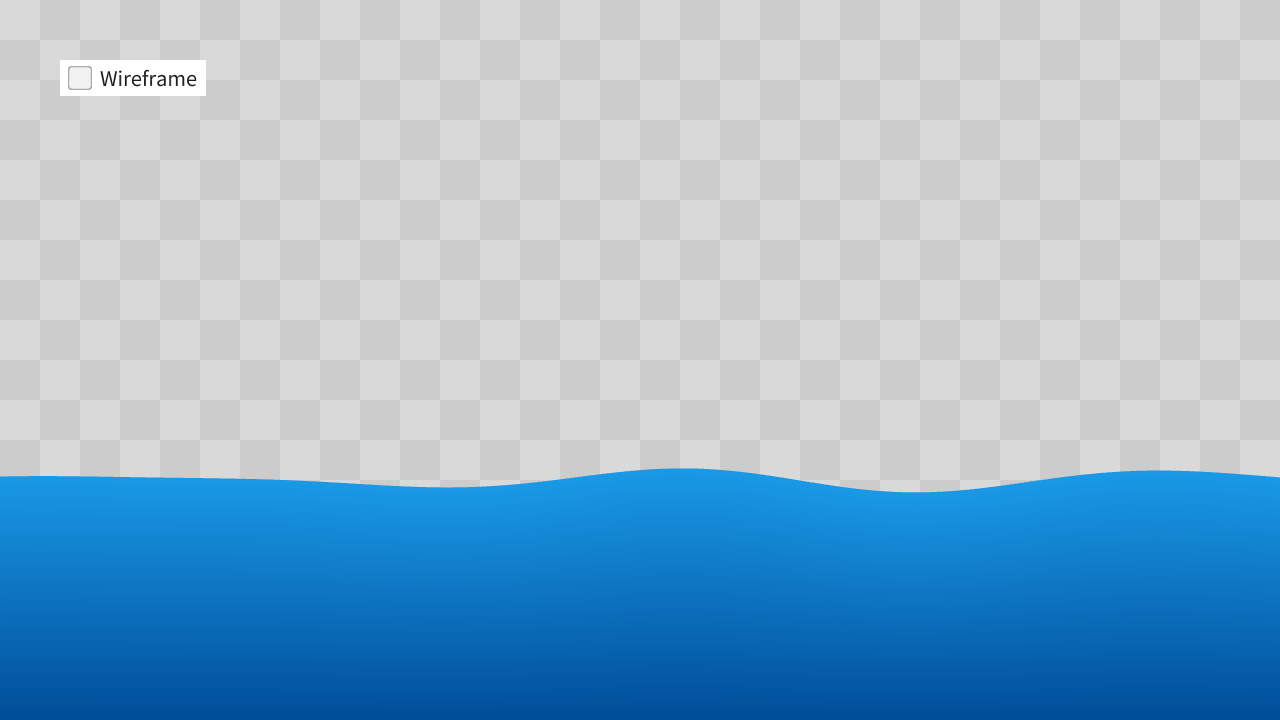

HLSL
namespace s3d
{
//
// VS Output
//
struct PSInput
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR0;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
//
// Siv3D Functions
//
float4 Transform2D(float2 pos, float2x4 t)
{
return float4((t._13_14 + (pos.x * t._11_12) + (pos.y * t._21_22)), t._23_24);
}
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
cbuffer VSConstants2D : register(b0)
{
row_major float2x4 g_transform;
float4 g_colorMul;
}
cbuffer SoftShape : register(b1)
{
float g_t;
}
//
// Functions
//
float CalcWave(float x, float t)
{
return sin(x * 0.011 + t) * 6
+ sin(x * 0.013 + -t * 1.1) * 4
+ sin(x * 0.017 + t * 1.3) * 3;
}
s3d::PSInput VS(uint id: SV_VERTEXID)
{
s3d::PSInput result;
float2 pos;
float4 color;
uint xi = (id / 6);
uint i = (id % 6);
if ((i == 0) || (i == 2) || (i == 3))
{
pos.x = (xi * 8);
}
else
{
pos.x = ((xi + 1) * 8);
}
if ((i == 2) || (i == 3) || (i == 5))
{
pos.y = 720;
color = float4(0.0, 0.3, 0.6, 1.0);
}
else
{
pos.y = 480 + CalcWave(pos.x, g_t);
color = float4(0.1, 0.6, 0.9, 1.0);
}
result.position = s3d::Transform2D(pos, g_transform);
result.color = color;
result.uv = float2(0, 0);
return result;
}
GLSL
# version 410
//
// VS Input (nothing)
//
//
// VS Output
//
layout(location = 0) out vec4 Color;
layout(location = 1) out vec2 UV;
out gl_PerVertex
{
vec4 gl_Position;
};
//
// Siv3D Functions
//
vec4 s3d_Transform2D(const vec2 pos, const vec4 t[2])
{
return vec4(t[0].zw + (pos.x * t[0].xy) + (pos.y * t[1].xy), t[1].zw);
}
//
// Constant Buffer
//
layout(std140) uniform VSConstants2D
{
vec4 g_transform[2];
vec4 g_colorMul;
};
layout(std140) uniform Wave
{
float g_t;
};
//
// Functions
//
float CalcWave(float x, float t)
{
return sin(x * 0.011 + t) * 6
+ sin(x * 0.013 + -t * 1.1) * 4
+ sin(x * 0.017 + t * 1.3) * 3;
}
void main()
{
vec2 pos;
vec4 color;
uint xi = (gl_VertexID / 6);
uint i = (gl_VertexID % 6);
if ((i == 0) || (i == 2) || (i == 3))
{
pos.x = (xi * 8);
}
else
{
pos.x = ((xi + 1) * 8);
}
if ((i == 2) || (i == 3) || (i == 5))
{
pos.y = 720;
color = vec4(0.0, 0.3, 0.6, 1.0);
}
else
{
pos.y = 480 + CalcWave(pos.x, g_t);
color = vec4(0.1, 0.6, 0.9, 1.0);
}
gl_Position = s3d_Transform2D(pos, g_transform);
Color = color;
UV = vec2(0, 0);
}
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void DrawBackground()
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < (Scene::Height() / 40); ++y)
{
for (int32 x = 0; x < (Scene::Width() / 40); ++x)
{
if (IsEven(x + y))
{
RectF{ (x * 40), (y * 40), 40 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.85 });
}
}
}
}
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.80 });
const VertexShader vs
= HLSL{ U"example/shader/hlsl/wave.hlsl" }
| GLSL{ U"example/shader/glsl/wave.vert", { { U"VSConstants2D", 0 } } };
if (not vs)
{
throw Error{ U"Failed to load a shader file" };
}
ConstantBuffer<float> cb;
bool showWireframe = false;
while (System::Update())
{
cb = static_cast<float>(Scene::Time());
DrawBackground();
{
Graphics2D::SetVSConstantBuffer(1, cb);
const ScopedRenderStates2D states{ showWireframe ? RasterizerState::WireframeCullNone : RasterizerState::Default2D };
const ScopedCustomShader2D shader{ vs };
// 頂点情報の無い三角形を 2 * 160 個描画する
// (頂点情報は頂点シェーダで設定する)
Graphics2D::DrawTriangles(2 * 160);
}
SimpleGUI::CheckBox(showWireframe, U"Wireframe", Vec2{ 60, 60 });
}
}
11.6 シェーダでの頂点生成の応用 ②¶
別のパターンもサンプルに収録されています。頂点位置の決定に CPU 側のプログラムは関与していません。
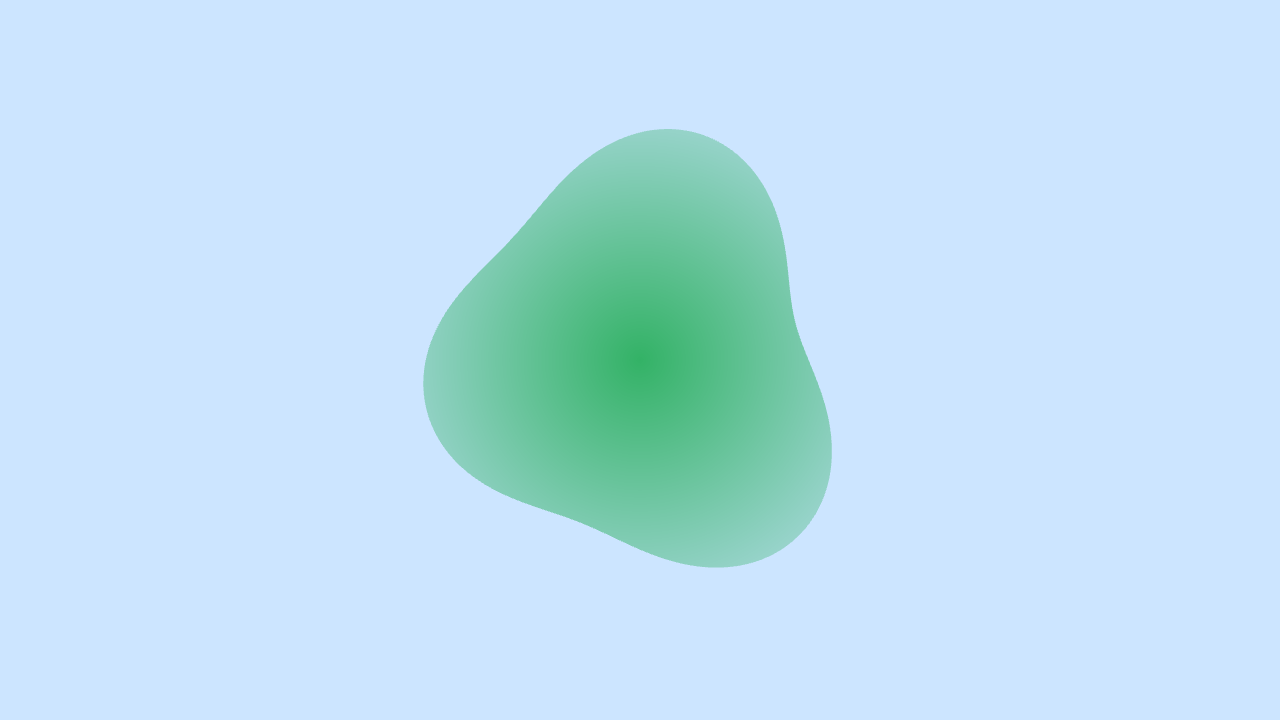

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Window::Resize(1280, 720);
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.8, 0.9, 1.0 });
const VertexShader vs
= HLSL{ U"example/shader/hlsl/soft_shape.hlsl" }
| GLSL{ U"example/shader/glsl/soft_shape.vert", { { U"VSConstants2D", 0 }, { U"SoftShape", 1 } }};
if (not vs)
{
throw Error{ U"Failed to load a shader file" };
}
ConstantBuffer<float> cb;
while (System::Update())
{
cb = static_cast<float>(Scene::Time());
{
Graphics2D::SetVSConstantBuffer(1, cb);
const ScopedCustomShader2D shader{ vs };
// 頂点情報の無い三角形を 360 個描画する
// (頂点情報は頂点シェーダで設定する)
Graphics2D::DrawTriangles(360);
}
}
}